Exothermic and Endothermic reactions
This content delves into exothermic and endothermic reactions, highlighting their impacts on temperature and surroundings. It discusses specific examples such as ammonium chloride and magnesium nitrate, detailing their properties and uses in various applications. The work presents a clear distinction between reactions that absorb heat, leading to cooling effects, and those that release heat, resulting in temperature increases. Accompanying images provide visual insights into these chemical processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Exothermic and Endothermic reactions By: Elena Sahawneh, Reine Talhami, Zaid elhalah, Mila kuzouz
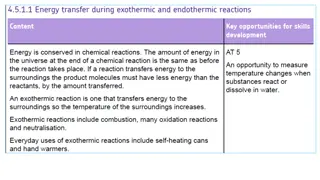
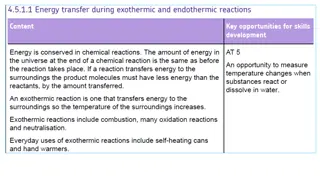
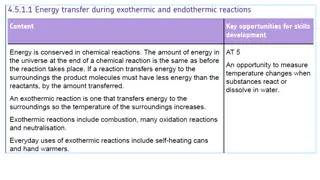
What are exothermic and endothermic changes in water An exothermic process releases heat, causing the temperature of the immediate surroundings to rise.An endothermic process absorbs heat and cools the surroundings.
Ammonium chloride properties Chemical formula: NH4Cl Properties: endothermic reaction when dissolved in water Has a boiling point at 338 C pH:4
Ammonium chloride uses Used as a yeast nutrient in breadmaking. Detergents Hair dye Dusting materials
Magnesium nitrate properties Chemical formula: Mg(NO3)2 Properties: exothermic reaction when dissolved in water Has a boiling point of 330 C pH:5-7
Magnesium nitrate uses Catalyst for growing crops Heart medicine Anti-anxiety medicine
Calcium hydroxide properties Chemical formula: Ca(OH) Properties: Exothermic reaction when dissolved in water Has a boiling point of 1,484 C pH:8
Calcium hydroxide uses in toothpaste Plant fertilizer Used to make cement
Potassium hydroxide Chemical formula: KOH Properties: exothermic reaction when dissolved in water Has a boiling point of 760 C
Potassium hydroxide uses Used in baking Used to manufacture soap In fruits such as bananas
Exothermic or Endothermic? Substances Initial temperature of the system Final temperature of the system Change in temperature Endothermic or exothermic Ammonium chloride 21 48 27 endothermic Magnesium nitrate 40 29.3 -10.7 exothermic Calcium hydroxide 60 24 -36 exothermic Potassium hydroxide 20 15.2 -4.8 exothermic