Initial Fluid Composition & Reaction Intervals in Groundwater Model
This groundwater modeling project focuses on specifying domains, defining reaction intervals, and setting fluid properties. It involves analyzing the flow of contaminated and clean water, simulating reactions over time intervals, and considering sorption effects on Pb++ transport. Various mass transport properties and sorbing surfaces are also defined to understand fluid dynamics and contaminant behavior in the aquifer system.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Specify domains starting fluid composition on the Initial pane Clean water
Define the reaction intervals. Specify what fluids flow into the domain, and when. Inlet fluid contaminated enters the domain from t = 0 to 2 years Inlet fluid flush enters the domain from t = 2 to 10 years Click to add a new reaction interval
The various inlet fluids are defined on the Fluids pane Inlet fluid named contaminated carries Pb++ and Br into domain The Br acts as a tracer in our model. Clean rinse water: negligible Pb++ and Br in the flush inlet fluid Click to add a new fluid
Specify domain size and gridding on the Domain pane. Domain is 1 km long, divided into 400 nodal blocks
Specify flow rate on the Flow pane. Set flowrate for 1st and 2nd reaction intervals individually, or set one flowrate for all intervals Set specific discharge or hydraulic head/ potential drop
Set various mass transport properties on the Medium pane. Porosity affects groundwater velocity. Used to calculate coefficient of hydrodynamic dispersion.
File Open Sorbing Surfaces Kd describes distribution coefficient between Pb++ and aquifer sediments. Br does not sorb. You can add any number of Kd, Freundlich, or Langmuir isotherms. You can also account for ion exchange or surface complexation using the two-layer model. Run Go traces the model
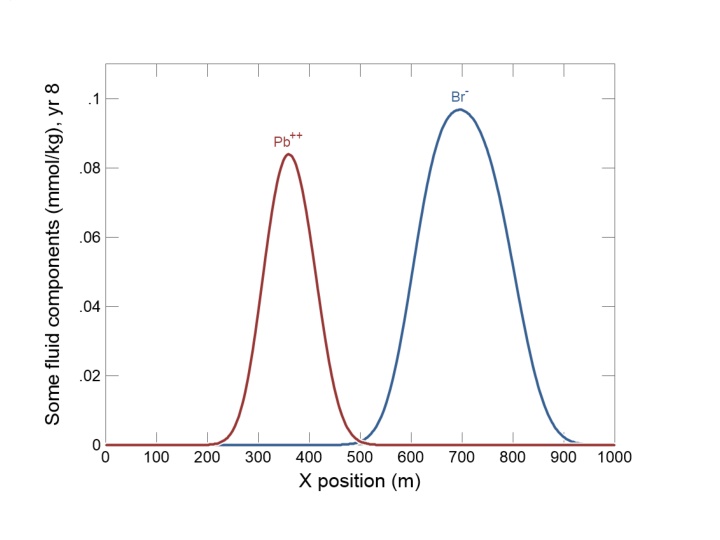
Sorption retards Pb++ transport relative to nonreactive tracer Br .