Introduction to Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Esters by Robert Wagner
"Learn about the properties and naming conventions of aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters in physical science. Understand the functional groups and chemical structures of these compounds, as well as their roles in scents and irritants."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Physical Science Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, & Esters Presented by Robert Wagner
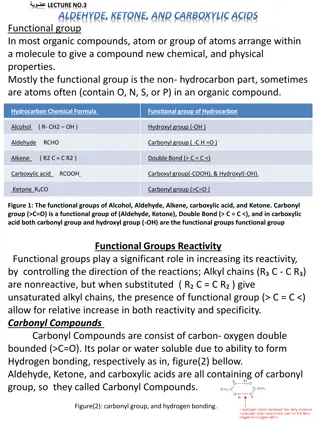
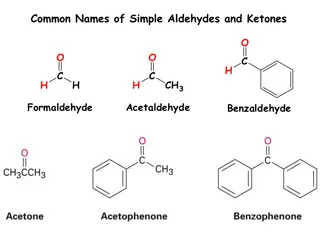
Aldehydes & Ketones The aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group This is a functional group with a carbon-oxygen double bond Naming - use the following suffixes Aldehydes -al Keytones - -one Image Credit: OpenStax Chemistry Chapter 20.3 CC BY 4.0
Aldehydes & Ketones The aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group This is a functional group with a carbon-oxygen double bond Naming - use the following suffixes Aldehydes -al Keytones - -one Image Credit: OpenStax Chemistry Chapter 20.3 CC BY 4.0
Carboxylic Acids and Esters Contain a carbonyl group with a second oxygen atom In a carboxylic acid, the second oxygen atom is bonded to a hydrogen atom In an ester, the second oxygen atom is bonder to another carbon atom Image Credit: OpenStax Chemistry Chapter 20.3 CC BY 4.0
Esters Many scents Have low vapor pressure since they do not have hydrogen bonds between molecules Image Credit: OpenStax Chemistry Example 20.8 CC BY 4.0
Discussion Simplest carboxylic acid: ???2? - Formic Acid Causes pain and irritation from ant and wasp sitings Acetic Acid - Vinegar ??3??2? Flowers, perfumes and fruits Aroma due to the presence of one or more esters
Summary Aldehydes & Ketones contain a functional group with a carbon-oxygen double bond Carboxylic Acids & Esters contain a carbonyl group with a second oxygen atom bonded to the carbonyl group Esters are responsible for many of the scents with which we are familiar