Keystroke-Level Model and Learning Goals
Explore the Keystroke-Level Model (KLM) by Niels Henze and understand its application in predicting task completion time. Learn the learning goals associated with KLM, and discover the operators and methods involved in executing tasks efficiently. Enhance your understanding of KLM with practical examples and insightful insights.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 1
Learning Goals Know what KLM stands for Know the KLM operators Being able to predict how long tasks take using KLM Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 2
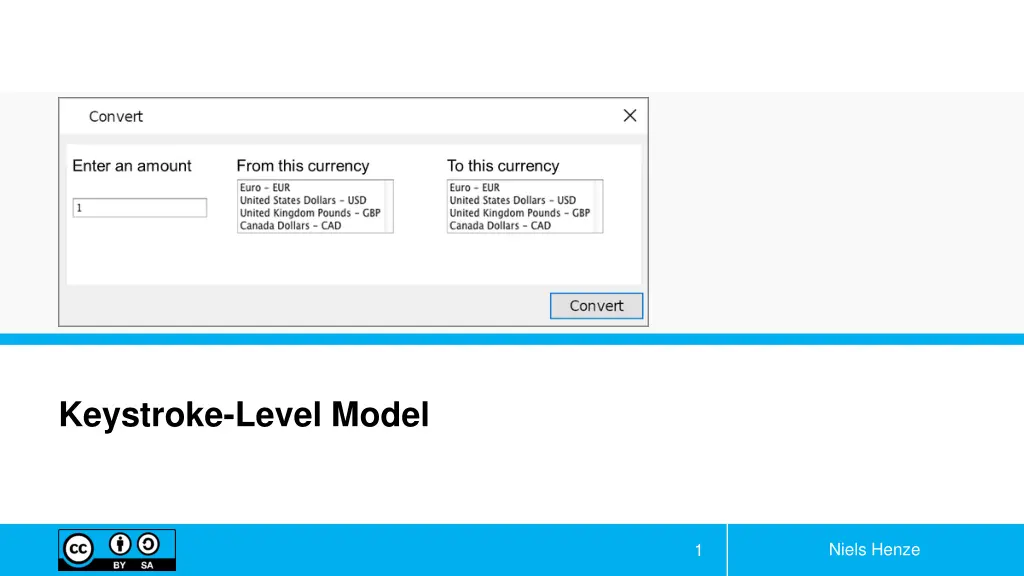
Summe Enter an amount From this currency To this currency 6 Task: Convert 12 Euro in US Dollar One hand on the mouse, nothing selected What do we need to know? Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 3
Task: Convert 12 Euro in US Dollar One hand on the mouse, nothing selected Summe Enter an amount From this currency To this currency 12 6 select text field delete value enter value select Euro select Dollar select Convert Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 4
Keystroke-Level Model (KLM) Simplified version of the "Goals, Operators, Methods, and Selections rules" (GOMS) Model KLM predicts how much time it takes to execute a task Execution of a task is decomposed into primitive operators Physical motor operators Pressing a button, pointing, drawing a line, Mental operator Preparing for a physical action System response operator User waits for the system to do something Keystroke-Level Model
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB P D(nD, lD) M R(t) Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 6
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time Expert typist (90 wpm): 0.12s Averaged skilled typist (55 wpm): 0.20s Average non-secretarial typist (40 wpm): 0.28 Worst typist (unfamiliar with keyboard): 1.2s H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB P D(nD, lD) M R(t) Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 7
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time Expert typist (90 wpm): 0.12s Averaged skilled typist (55 wpm): 0.20s Average non-secretarial typist (40 wpm): 0.28 Worst typist (unfamiliar with keyboard): 1.2s 0.4s H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB P D(nD, lD) M R(t) Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 8
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time Expert typist (90 wpm): 0.12s Averaged skilled typist (55 wpm): 0.20s Average non-secretarial typist (40 wpm): 0.28 Worst typist (unfamiliar with keyboard): 1.2s 0.4s H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB 0.1s / 2*0.1s P D(nD, lD) M R(t) Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 9
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time Expert typist (90 wpm): 0.12s Averaged skilled typist (55 wpm): 0.20s Average non-secretarial typist (40 wpm): 0.28 Worst typist (unfamiliar with keyboard): 1.2s 0.4s H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB 0.1s / 2*0.1s P 0.8s to 1.5s with an average of 1.1s Can also use Fitts Law D(nD, lD) M R(t) Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 10
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time Expert typist (90 wpm): 0.12s Averaged skilled typist (55 wpm): 0.20s Average non-secretarial typist (40 wpm): 0.28 Worst typist (unfamiliar with keyboard): 1.2s 0.4s H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB 0.1s / 2*0.1s P 0.8s to 1.5s with an average of 1.1s Can also use Fitts Law 0.9s*nD + 0.16*lD D(nD, lD) M R(t) Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 11
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time Expert typist (90 wpm): 0.12s Averaged skilled typist (55 wpm): 0.20s Average non-secretarial typist (40 wpm): 0.28 Worst typist (unfamiliar with keyboard): 1.2s 0.4s H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB 0.1s / 2*0.1s P 0.8s to 1.5s with an average of 1.1s Can also use Fitts Law 0.9s*nD + 0.16*lD D(nD, lD) M 1.35s R(t) Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 12
Operator K Description Keystroke, typing one letter, number, etc. or function key such as CRTL or SHIFT Associated Time Expert typist (90 wpm): 0.12s Averaged skilled typist (55 wpm): 0.20s Average non-secretarial typist (40 wpm): 0.28 Worst typist (unfamiliar with keyboard): 1.2s 0.4s H Homing , moving the hand between mouse and keyboard Pressing (B) or clicking (BB) a button Pointing with a mouse to a target Drawing nD straight line segments of length lD Subsumed time for mental acts; sometimes used as look-at System response time, time during which the user cannot act B/BB 0.1s / 2*0.1s P 0.8s to 1.5s with an average of 1.1s Can also use Fitts Law 0.9s*nD + 0.16*lD D(nD, lD) M 1.35s R(t) Dependent on the system Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 13
Task: Convert 12 Euro in US Dollar One hand on the mouse, nothing selected select text field delete value enter value select Euro select Dollar select Convert P, BB H, K M, K, K H, M, P, BB M, P, BB P, BB Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 14
select text field delete value enter value select Euro select Dollar select Convert P, BB H, K M, K, K H, M, P, BB M, P, BB P, BB Operator Times: P 1.1s M = 1.35s B = 0.1s K = 0.28s H = 0.4s 4*P = 8*B = 2*H = 3*M = 3*K = Total = 4.40s 0.80s 0.80s 4.05s 0.84s 10,89s Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 15
Hand on mouse, nothing selected, go to photo: Which is the fastest interface? Which is the slowest? Version 1 Version 2 Version 3 Version 4 Keystroke-Level Model Niels Henze 16
Wrap-up The Keystroke-Level Model predicts task completion time for simple dialogs Assumes a trained average user Especially useful to compare alternatives Using KLM by hand can become lengthy and complex KLM is not useful for tasks that require reasoning Niels Henze 17
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 (CC BY-SA) license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0 Attribution: Niels Henze For more content see: https://hci-lecture.de Niels Henze 18