Lipids: Structures, Functions, and Hydrolysis
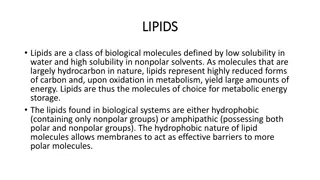
Lipids are diverse molecules with important roles in the body, including structural components, energy storage, and insulation. They can be classified based on their structure and behavior in hydrolysis reactions. Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids exhibit different properties, affecting their melting points and functions. Triacylglycerols, the most common lipid class in nature, consist of glycerol esterified with fatty acids. Explore the fascinating world of lipids and their significance in biochemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
HELPING STUDENTS REVISE KNOWLEDGE MARZANO S SUPER 7 ELEMENT 20 *Review IS NOT Revision*
PURPOSE Revising knowledge to help students examine their own deeper understanding of critical content and essential learning is a very important step in the learning process for all learners in all contexts. Revising asks: Based on what I just learned, what do I know now?
CONNECTIONS TO OTHER ELEMENTS Student revision should not occur in isolation. Occurs with the student dominated elements of Design Question 2 processing, elaborating, recording, and reflecting. Revision also connects different chunks of content. Prepares students for more complex tasks required to meet the rigor of the standards being taught. A critical bridge between different chunks of new knowledge gained as well as to more complex tasks.
TEACHER EVIDENCE Focus The teacher engages students in revision of previous knowledge about content addressed in previous lessons. Asks students to examine previous entries in their academic notebooks or notes Engages the whole class in an examination of how the current lesson changed perceptions and understandings of previous content Has students explain how their understanding has changed
STUDENT EVIDENCE Make connections to information previously recorded about content When asked, can explain previous errors or misconceptions they had about content
HOW TO TEACH STUDENTS TO REVISE THEIR LEARNING 1) Review/revisit prior understanding of content 2) Identify and correct mistakes or misconceptions 3) Self identify gaps in knowledge and fill in those gaps 4) Decide where to amend the learning 5) Explain the reason for the revision to the learning
STRATEGIES FOR IMPLEMENTATION 1) Sentence Starters I just learned that ; I changed my thinking about ; I used to think ___, but now I think 2) Graphic Organizers with Revision Structures Left side I knew this ; based on new learning, Right side I now know 3) Cornell Notes 4) Academic (Interactive) Notebooks students revise previous learning & build their new learning towards meeting the rigor of the standard(s); revision becomes a normal routine in the learning cycle 5) Peer Reviews utilizing a rubric, peers can provide safe feedback to each other with the follow-up opportunity for the student to revise the product/learning/thinking
STRATEGIES FOR IMPLEMENTATION (cont d) 6) Open ended follow-up questions asking deeper thinking questions that goes beyond what was explicitly taught and/or make connections to previous learning with the unit of instruction 7) Using visual/pictorial structures having students add on to a complex visual representation of content over time as new learning is incorporated into previous learning 8) Homework/classwork Revision during a review of homework/classwork, allow students to make changes to their work prior to submission. This can be done in a different color ink to allow the teacher to see the initial misconceptions as well as the revision to a student s learning.
MIND MAPPING ACTIVITY *WORD ASSOCIATION* Write the term given to your group by the facilitator, nice and BIG, in the center of your large poster paper Each group member should have their own marker/pen and some post-its You will have 1 minute to silently brainstorm as many words and phrases that are related to the key term as possible Write them on the post-its and place on the paper
WHEN TIME IS CALLED Rotate to the next table and continue the process Don t read what others have written! Think for yourself and fill the paper with as many post-its as possible
MAKE A COMPLETE ROTATION VISIT EACH TABLE!
RETURN TO YOUR ORIGINAL SPOT
ORGANIZE THE IDEAS Clear all post-its from the paper Categorize the thoughts
REARRANGE POST-ITS Cluster the post-its back on the paper in a way that makes sense to your group Draw a shape (circle, square, etc.) around each cluster as a barrier; try to use a different color for each cluster Devise a category title for each cluster and clearly label each with the new title
THE RULES 1) Begin with a central image of 3 or more colors 2) Make the lines connecting to center image thicker and curved, like the branch of a tree 3) For the lines connected to central image, use only one key word per branch (these are your categories) 4) PRINT all words 5) Make line length equal to word length 6) Try to have an image for each branch (category) 7) Keep your paper placed horizontally before you; there should be no turning of the paper to read the completed map
SHARE YOUR MAPS