Musculoskeletal System Part 5- The Muscles
Muscle tissue is contractile and allows for movement in different parts of the body. Learn about the characteristics and functions of skeletal, smooth, and other types of muscle tissues, as well as their roles in voluntary and involuntary movements.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
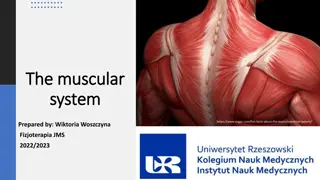
Musculoskeletal System Part 5 The Muscles September 2021 Dr. Anna Haro Westside HS
LEARNING Objectives TEKS: 130.231.(c)(1)(A, & B) and 130.231.(c)(2)(A, B, C, F, & G) & (3)(B) Students will apply previous knowledge of human and cellular biology. Students will compare and contrast the three types of muscle tissue.
Objetivos de aprendizaje TEKS: 130.231.(c)(1)(A, & B) and 130.231.(c)(2)(A, B, C, F, & G) & (3)(B) . Los estudiantes aplicar n conocimientos previos de biolog a humana y celular. Los estudiantes comparar n y contrastar n los tres tipos de tejido muscular.
General characteristics of muscle tissue Muscle tissue, or muscle fiber is contractile = this means the muscle cells or fibers can shorten and thicken. Muscle cells are elongated and thin or spindle- shaped. They are called myocytes. As the muscle cells contract, the muscle fibers pull at the attached ends, shortening the muscle and moving the associated body part(s). The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, smooth, and _______________________.
Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle attaches to bone (via tendons) for movement. Skeletal muscle controls voluntary movement through the somatic nervous system. (The brain sends a signal down the spinal cord to the peripheral nerve which stimulates the muscle to contract, causing movement.) Skeletal muscle cells are long and very narrow (almost 2 inches in length, approximately 4 cm and only 0.1mm in width) Alternating light and dark cross-markings on muscle cells are called striations. Muscle cells are multinucleate, meaning many ________________. Skeletal muscle is located in the head, trunk, extremities, allowing gross and fine motor _______________, such as facial expressions, writing, talking, standing, walking, and more.
Skeletal muscle https://en.wikipedia.org/wi ki/Striated_muscle_tissue https://www.scientistcindy. com/muscle-physiology.html
Smooth muscle Smooth muscle is called smooth because it lacks striations and looks smooth. Smooth muscle cells are shorter and spindle shaped. Smooth muscle cells contain one centrally-located ________________. Smooth muscle controls involuntary movement through the autonomic nervous system. Smooth muscle is located in the bladder, intestine, stomach, interior walls of the blood vessels, and the inside of the hollow organs. https://www.shutterstock.com/image- photo/smooth-muscle-fibers-small- intestine-longitudinally-750031276
Cardiac muscle is found only in the ______________. Cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) are striated and joined end-to-end. Cardiac muscle cells are branched and interconnected forming complex networks. Cardiac muscle tissue is involuntary and can function without an intact nervous system stimulation (Discussion question: How is this possible?) Cardiomyocytes contain a single ________________. Cardiac muscle Image from: https://www.gettyimages.com/photo s/cardiac-muscle-tissue
Questions about the muscles? I don t have most of the answers, but I can help you find the right references. Remember the HON-code? https://www.hon.ch/HONcode/
References 1. Shier D, Butler J, Lewis R. Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9th edition, McGraw Hill Education Publishing, 2002. 2. Images cited in the corresponding slides.