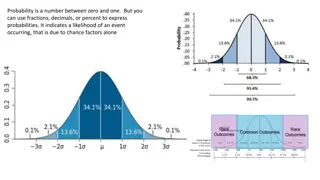
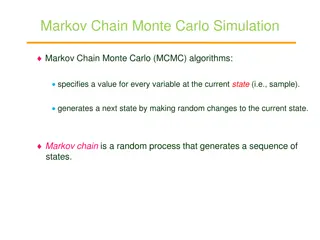
Probability Distributions in Statistical Learning
Explore the concepts of probability distributions in statistical learning through hands-on activities using playing cards. Students engage in simulations to compare theoretical and empirical probabilities, calculate expected values and standard deviations, and deepen their understanding of variance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Subject Botany Class B.Sc. II Session 2018-19 Week wise division of Syllabus Semester III Paper 5- Diversity and Systematics of Gymnosperms 1stto 4thweek Syllabus 1. General features of Gymnosperms 2.Classification of Gymnosperms 3. Fossil Gymnosperms(Pento xylon, cordaites , Bennettites,Glossopteris , lyginopteris , williamsonia 4. Distribution of Gymnosperms 5. Cytology of Gymnosperms 6. Economic importance of Indian Gymnosperms 7. General characters of pro Gymnosperms , Morphological features of Arachaeopteries and Aneurophyton 8. Gerneral characters of Cycadales and Ephedrales , Morphology <anatomy reproduction and Life cycle of Cycas and Ephedra 5th to 8th week Syllabus 1.Gerneral characters of Coniferales and Gnetales 2. Morphology, Anatomy Reproduction and life Cycle of Pinus and Gnetum 3. Origin and evolution of angiosperms giving suitable examples. 4. Primitive and advance characters of angiosperms 9thto 12thweek syllabus 1. Angiosperms taxonomy/brief history,aims and fundamental components (alpha taxonomy,beta- taxonomy And omega-taxonomy . 2. Identification keys ,ICBN ,principles and rules,taxonomic ranks ,type concept 3. Classification of angiosperms
4. Salients features,comparison ,merits and demerits classification systems purposed by Bentham and Hooker and Engler and Prantl. 13th to 15th week syllabus and revision Diagonostic features,technical description and taxonomic significance of flowering plants of families 1. Ranunculaceae 2. Brassicaceae 3. Malvaceae 4. Rutaceae 5. Fabaceae 6. Apiaceae 7. Cucurbitaceae 8. Rosaceae 9. Apocynaceae 10. Asclepiadaceae 11. Solanaceae 12. Laminaceae 13. Euphorbiaceae 14. Asteraceae 15. Lilliaceae 16. Poaceae
Semester -4th Paper-Plant Anatomy 1 to 4th week syllabus 1. Tissue Systems: Epidermal: Structure and types of stomata, idioblasts, trichomes, nectaries, hydathodes. Fundamental: parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma; Vascular system. 2. The root system: the root apical meristem and its histological organization; anatomical details of Dicot and Monocot roots. 5th to 8th week syllabus 3. The shoot system: The shoot apical meristem and its histological organization. Anatomical details of Dicot and Monocot stems. Cambium and its functions. Secondary growth including anomalous secondary growth 4. Leaf: Anatomy in Dicots and Monocots and modification with special reference to their function
Paper-VIII: DEVELOPMENT AND REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS Week 9th to 12th syllabus 1. Vegetative Reproduction: Various methods of vegetative propagation and applications in floriculture and horticulture. 2. Flower: a modified shoot; structure, development of flower; Inflorescence types; structure of anther and pistil. Week 13th to 16th syllabus 3. Male and female gametophyhtes; types of pollination; pollen-pistil interaction, self incompatibility, double fertilization. 4. Post fertilization changes, endosperm and embryo development; seed development, structure and dispersal; dormancy fruit development and types of fruit.
B.Sc. (Botany) Part-III (SEMESTER-V) PAPER IX: PLANT PHYSIOLOGY Week 1th to 4th syllabus 1. Plant-water relations: Importance of water to plant life; diffusion and osmosis; absorption, transport of water and transpiration; mechanism of stomatal opening and closing. 2. Mineral nutrition: Essential macro- and micro- elements and their role; mineral uptake; deficiency and toxicity symptoms. 3. Transport of organic substances: Mechanism of phloem transport; source- sink relationship; factors affecting translocation. 4. Basics of enzymology: Discovery and nomenclature; characteristics of enzymes; concepts of holoenzyme, apoenzyme, coenzyme and cofactors; regulation of enzyme activity; mechanism of action. Week 5th to 8th syllabus 5. Photosynthesis: Significance; historical aspects; photosynthetic pigments; action spectra and enhancement effect; concept of two photosystems; Z-scheme; photophosphorylation; Calvin cycle; C4 pathway; CAM plants; photorespiration. 6. Respiration: ATP- the biological energy currency; aerobic and anaerobic respiration; Kreb s cycle; electron transport mechanism (chemi- osmotic theory) redox potential; oxidative phosphorylation; pentose phosphate pathway. 7. Nitrogen metabolism: Biology of nitrogen fixation; importance of nitrate reducatse and its regulation; ammonium assimilation. 8. Lipid metabolism: Structure and function of lipids; fatty acid biosynthesis; - oxidation; saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
PAPER X: PLANT GROWTH, DEVELOPMENT AND BIOTECHNOLOGY Week 9th to 12th syllabus SEM 5 1. Growth, phases of growth, growth kinetics; plant hormones: discovery, bioassay, physiological effects and application of auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abcissic acid and ethylene. 2. Photomorphogenesis, discovery, structure, physiological role and mechanism of action of phytochrome and cryptochrome. 3. Photoperiodism, vernalization, biological clocks, physiology of senescence and abscission. 4. Physiology of seed dormany and seed germination; plant movements. Week 13th to 16th syllabus 5. Tools and techniques of recombinat DNA technology with special reference to restriction enzymes, gel electrophoresis, Southern blotting, cloning vectors and PCR. Genomic and cDNA library. 6. Techniques of gene mapping and chromosome walking; methods of gene transfer in plants. 7. Basic concept of plant tissue, culture, totipotency, micropropagation, anther culture, embryo culture, synthetic seeds and somatic hybridization. 8. Biotechnology and its application in human welfare with particular reference to industry, plant breeding and molecular farming.
PAPER XI: PLANT ECOLOGY SEM-6 Week 1st to 4th syllabus 1. Concept of ecology and its scope. Environmental factors: climatic, edapic, topographic and biotic, Shelfords law of tolerance. 2. Population ecology: Characteristics, positive and negative interaction, growth forms, carrying capacity, ecotypes and ecads. 3. Community ecology: Community characteristics, frequency, density and abundance, cover, life forms. ecological succession (Hydrosere, Xerosere). Gause principle of competitive exclusion. 4. Structure and concept of ecosystem, ecological pyramids, food chain, food web, ecological energetics, ecological productivity. Week 5th to 8th syllabus 5. Environmental issues: Brief idea of air, water, noise and soil pollution. Global warming and ozone depletion. International efforts for mitigation of global climate change. 6. Biodiversity: Introduction and Importance of Biodiversity; Elements of Biodiversity; Genetic, species and ecological diversity. Conservation strategies, concept of hot spots, biomes, phytogeographic regions of India, vegetation types (Forests, Grasslands, Desserts and Wetlands). 7. Ecological adaptations in xerophytes, hydrophytes and halophytes. 8. Biogeochemical cycles with particular reference to C, N and P.
PAPER XII: PLANT UTILIZATION SEM-6 Week 9th to 12th syllabus 1. The importance and nature of plant products; fibres: surface fibres (cotton), soft fibres (Jute), hard fibres (Coir). Forest products: Wood, properties, seasoning and importance, important timber plants of India. 2. Brief history of origin of food plants; cultivation practice and recommended varieties of wheat, rice, maize and sugarcane with particular reference to Punjab. 3. Cultivation practices and use of soyabean, sunflower, mustard, groundnut and coconut. 4. Vegetables and Fruits: Botanical name, family, season and area of cultivation of potato, tomato, brinjal, carrot, ladyfinger, pea, mango, apple, banana, guava, kinnow and grapes. Week 13th to 16th syllabus and revision 5. Spices: General account pertaining to botanical name, family and part used in case of clove, cardamom, black pepper, turmeric, cumin and ginger. 6. Medicinal Plants: General account pertaining to botanical name, family, part used and active principle in case of belladonna, neem, tulsi, stevia, rauwolfia, ashwagandha and glycyrrhiza. 7. Beverages and Narcotics: Cultivation practices, botanical name, family and active ingredients of tea and coffee. Cannabis, tobacco and opium. 8. Rubber: Major sources, cultivation, processing and uses of Para rubber.