Properties of Ionic and Metallic Bonds
This content discusses the characteristics and behaviors of ionic and metallic bonds in compounds formed from metals combined with non-metals. It covers the concept of oppositely charged ions, the sharing of electrons in covalent bonds, and the importance of delocalized electrons in metallic structures. The limitations of a simple model are highlighted, along with the properties of different states of matter and the unique properties of ionic and metallic compounds.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
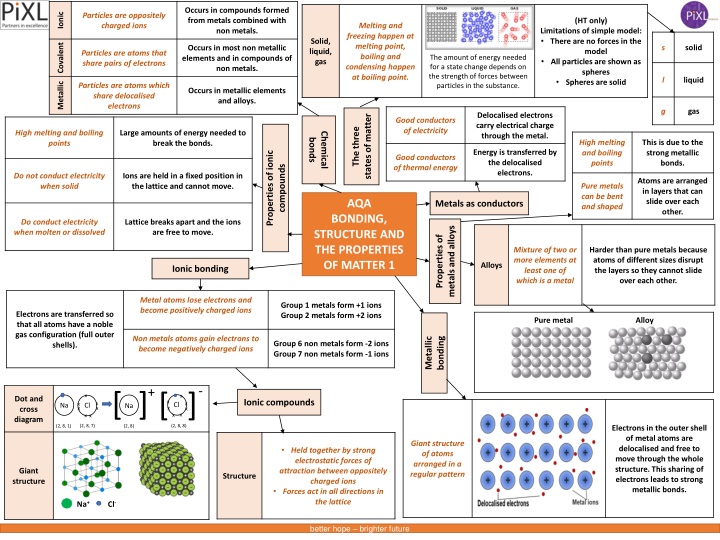
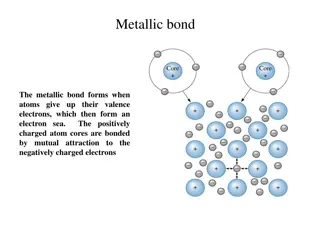
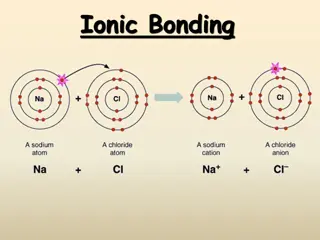
Occurs in compounds formed from metals combined with non metals. Particles are oppositely charged ions Ionic (HT only) Melting and freezing happen at melting point, boiling and condensing happen at boiling point. Limitations of simple model: There are no forces in the model All particles are shown as spheres Spheres are solid Solid, liquid, gas Covalent s solid Occurs in most non metallic elements and in compounds of non metals. Particles are atoms that share pairs of electrons The amount of energy needed for a state change depends on the strength of forces between particles in the substance. l liquid Metallic Particles are atoms which share delocalised electrons Occurs in metallic elements and alloys. g gas Delocalised electrons carry electrical charge through the metal. states of matter Good conductors of electricity The three High melting and boiling points Large amounts of energy needed to break the bonds. Chemical bonds High melting and boiling points This is due to the strong metallic bonds. Properties of ionic Energy is transferred by the delocalised electrons. Good conductors of thermal energy compounds Do not conduct electricity when solid Ions are held in a fixed position in the lattice and cannot move. Atoms are arranged in layers that can slide over each other. Pure metals can be bent and shaped AQA Metals as conductors BONDING, STRUCTURE AND THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1 Do conduct electricity when molten or dissolved Lattice breaks apart and the ions are free to move. metals and alloys Properties of Mixture of two or more elements at least one of which is a metal Harder than pure metals because atoms of different sizes disrupt the layers so they cannot slide over each other. Alloys Ionic bonding Metal atoms lose electrons and become positively charged ions Group 1 metals form +1 ions Group 2 metals form +2 ions Electrons are transferred so that all atoms have a noble gas configuration (full outer shells). Pure metal Alloy Metallic Non metals atoms gain electrons to become negatively charged ions bonding Group 6 non metals form -2 ions Group 7 non metals form -1 ions - + [ ] [ ] (2, 8, 8) x x Dot and cross diagram Ionic compounds x x x x xx Cl Na Cl Na x x x x x x (2, 8, 7) (2, 8, 1) (2, 8) Electrons in the outer shell of metal atoms are delocalised and free to move through the whole structure. This sharing of electrons leads to strong metallic bonds. Giant structure of atoms arranged in a regular pattern Held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions Forces act in all directions in the lattice Giant structure Structure Na+ Cl- better hope brighter future
Occurs in compounds formed from metals combined with non metals. Particles are oppositely charged ions (HT only) Melting and freezing happen at melting point, boiling and condensing happen at boiling point. Limitations of simple model: There are no forces in the model All particles are shown as spheres Spheres are solid solid Occurs in most non metallic elements and in compounds of non metals. Particles are atoms that share pairs of electrons The amount of energy needed for a state change depends on the strength of forces between particles in the substance. liquid Particles are atoms which share delocalised electrons Occurs in metallic elements and alloys. gas Delocalised electrons carry electrical charge through the metal. states of matter Good conductors of electricity The three High melting and boiling points Large amounts of energy needed to break the bonds. Chemical bonds High melting and boiling points This is due to the strong metallic bonds. Properties of ionic Energy is transferred by the delocalised electrons. Good conductors of thermal energy compounds Do not conduct electricity when solid Ions are held in a fixed position in the lattice and cannot move. Atoms are arranged in layers that can slide over each other. Pure metals can be bent and shaped AQA Metals as conductors BONDING, STRUCTURE AND THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1 Do conduct electricity when molten or dissolved Lattice breaks apart and the ions are free to move. metals and alloys Properties of Mixture of two or more elements at least one of which is a metal Harder than pure metals because atoms of different sizes disrupt the layers so they cannot slide over each other. Ionic bonding Metal atoms lose electrons and become positively charged ions Group 1 metals form +1 ions Group 2 metals form +2 ions Electrons are transferred so that all atoms have a noble gas configuration (full outer shells). Metallic Non metals atoms gain electrons to become negatively charged ions bonding Group 6 non metals form -2 ions Group 7 non metals form -1 ions - + [ ] [ ] (2, 8, 8) x x Ionic compounds x x x x xx Cl Na Cl Na x x x x x x (2, 8, 7) (2, 8, 1) (2, 8) Electrons in the outer shell of metal atoms are delocalised and free to move through the whole structure. This sharing of electrons leads to strong metallic bonds. Giant structure of atoms arranged in a regular pattern Held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions Forces act in all directions in the lattice Na+ Cl- better hope brighter future
Occurs in compounds formed from metals combined with non metals. (HT only) Limitations of simple model: There are no forces in the model All particles are shown as spheres Spheres are solid solid Occurs in most non metallic elements and in compounds of non metals. The amount of energy needed for a state change depends on the strength of forces between particles in the substance. liquid Occurs in metallic elements and alloys. gas Delocalised electrons carry electrical charge through the metal. states of matter The three Large amounts of energy needed to break the bonds. Chemical bonds This is due to the strong metallic bonds. Properties of ionic Energy is transferred by the delocalised electrons. compounds Ions are held in a fixed position in the lattice and cannot move. Atoms are arranged in layers that can slide over each other. AQA Metals as conductors BONDING, STRUCTURE AND THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1 Lattice breaks apart and the ions are free to move. metals and alloys Properties of Harder than pure metals because atoms of different sizes disrupt the layers so they cannot slide over each other. Ionic bonding Metal atoms lose electrons and become positively charged ions Metallic Non metals atoms gain electrons to become negatively charged ions bonding - + [ ] [ ] (2, 8, 8) x x Ionic compounds x x x x xx Cl Na Cl Na x x x x x x (2, 8, 7) (2, 8, 1) (2, 8) Electrons in the outer shell of metal atoms are delocalised and free to move through the whole structure. This sharing of electrons leads to strong metallic bonds. Held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions Forces act in all directions in the lattice better hope brighter future
solid ( liquid gas states of matter The three Chemical bonds Properties of ionic compounds AQA Metals as conductors BONDING, STRUCTURE AND THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1 metals and alloys Properties of Alloys Ionic bonding Metal atoms Metallic bonding Non metals atoms x Ionic compounds x xx Na Cl x x x better hope brighter future