Understanding AID Allocation for Non-AP MLDs in IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1
Explore the complex AID allocation rules for non-AP MLDs in the context of IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1. The document delves into issues related to AID assignment to legacy and non-AP MLDs, proposing solutions to ensure unique and reserved AID allocation for maximum efficiency in WLAN networks.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
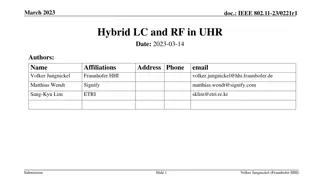
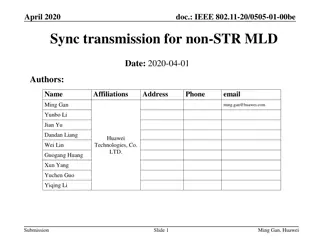
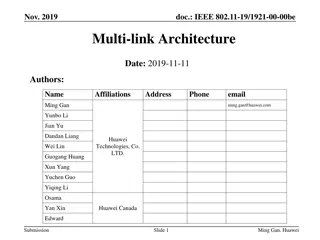
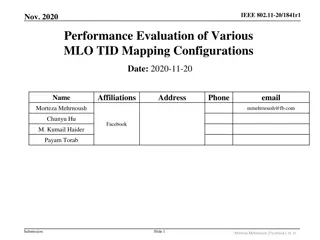
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 MLO: AID Allocation Date: 2020-04-28 Authors: Affiliations Address Phone email Name Young Hoon Kwon Liwen Chu Manish Kumar Hongyuan Zhang Yan Zhang Rui Cao Sudhir Srinivasa Hui-Ling Lou NXP Submission Slide 1 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 Background Current consensus includes: A bit in a partial virtual bitmap of a TIM element that corresponds to a non-AP MLD is set to 1 if any individually addressed BUs for the non-AP MLD are buffered by the AP MLD. This implies that an AID is allocated to each non-AP MLD regardless of the number of links the non-AP MLD has set up. In this contribution, we study if there are any further restrictions needed on the AID allocation for non-AP MLDs. Submission Slide 2 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 Background Baseline AID allocation rule: AID 0 is used to indicate group addressed traffic. When a multi-BSSID is supported, AIDs from 1 to (2^n -1) are not allocated to a STA, where the maximum possible number of BSSIDs is an integer power of 2, n = log2 (maximum possible number of BSSIDs) The bits 1 to (2^n 1) of the bitmap are used to indicate that one or more group addressed frames are buffered for each AP corresponding to a nontransmitted BSSID and are called NonTxBSS identifiers. The NonTxBSS ID equals the value carried in the BSSID Index field of the Multiple BSSID-Index element carried in its nontransmitted BSSID profile. AIDs from 2^n to 2007 are allocated to STAs within any BSS corresponding to a transmitted or nontransmitted BSSID. Submission Slide 3 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 Issues Let us assume that AP1 and AP2 are affiliated with an AP MLD: AP1 supports multiple BSSID such that the maximum possible number of BSSIDs for AP1 is 2^n. AP1 can assign STAs AID chosen from 2^n to 2007. AP2 does not operate with a multiple BSSID set. AP2 can assign STAs AIDs chosen from 1 to 2007. If AIDs 1 to (2^n-1) are assigned to legacy or single-link STAs: In TIM element sent by AP2, these AIDs indicate buffer status of the STAs and there s no issue. If AIDs 1 to (2^n-1) are assigned to non-AP MLDs: In TIM element sent by AP2, these AIDs indicate buffer status of the non-AP MLDs and there s no issue. In TIM element sent by AP1, these AIDs are doubly defined for both non-AP MLDs and the nontransmitted BSSIDs. Submission Slide 4 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 Solution As AID is assigned to an MLD level: The AID assigned to a non-AP MLD shall be unique and shall be not reserved on any link An AID less than 2^n where n is the maximum value of the MaxBSSID Indicator in a multiple BSSID set is reserved In other words, if there are N configured links for an AP MLD: AIDs from 1 to max(2^n_1, 2^n_2, 2^n_N) - 1 are not allocated to a non-AP MLD, where the maximum possible number of BSSIDs on i-th link is an integer power of 2, n_i = log2(maximum possible number of BSSIDs on i-th link) Submission Slide 5 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 Operation example MLD1 includes 3 APs in 3 links (Link1/2/3). BSSID of AP1a on Link1 is transmitted BSSID and AP2b on Link2 and AP3c on Link3 ARE nontransmitted BSSIDs. The number of nontransmitted BSSIDs within a set of Multiple BSSID set on each link is different: AP1a: 1, AP2a: 3, AP3a: 3 AIDs from 1 to max(1, 3, 3)=3 are not assigned to a non-AP MLD by MLD1. AID = 2 & 3 still can be assigned to legacy STA or a single-link STA on link1. : transmitted BBSID Link1 AP1a AP1b : nontransmitted BBSID Link2 AP2c AP2b AP2a AP2d Link 3 AP3c AP3d AP3b AP3a : MLD1 Submission Slide 6 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 Summary Baseline AID allocation rule is extended to cover non- AP MLDs. Submission Slide 7 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)
4/28/2020 Doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/0770r1 SP Do you support in TGbe SFD that The AID assigned to a non-AP MLD shall be unique and shall be set to a value greater than or equal to 2^n where n is the maximum value of the MaxBSSID Indicator amongst the multiple BSSID set(s) operating on any link of the AP MLD. Submission Slide 8 Young Hoon Kwon et al (NXP)