Understanding Cells: Theory, Structure, and Functions
Explore the fascinating world of cells through the Cell Theory, differences between animal and plant cells, functions of organelles, and the characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Learn about the basic units of life and the distinct features that define various types of cells.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Cell Theory (Theodor Schwann) 1. All living organisms are made of either one (unicellular) or more cells (multi cellular). 2. The cell is the basic unit of life. 3. All cells arise from pre- existing cells.
Similarities between animal and plant cell : - both have nucleus -both have membrane bound organelles - both have cytoplasm Differences between animal and plant cell : - shape - vacuole (size) - size - Plant cell has a rigid cell wall in addition to cell membrane and it has chloroplast.
WALT know the functions of the organelles in a cell. http://sciencespot.net/Media/CellsOrganelles Wkst.pdf
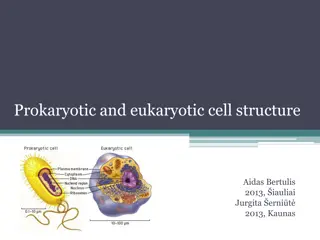
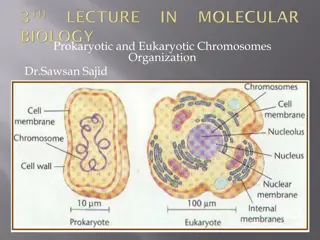
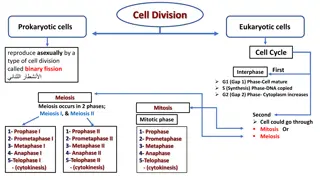
Prokaryotic Cell - Bacteria are prokaryotes, lacking well- defined nuclei and membrane-bound organelles. Have many shapes and sizes, from minute spheres, cylinders and spiral threads to flagellated rods and filamentous chains. Found practically everywhere on Earth and live in some of the most unusual and seemingly inhospitable places. - -
Eukaryotic Cell - An animal cell has several membrane-bound organelles. - The genetic material DNA resides mainly in the nucleus, which is surrounded by a double membrane with numerous openings called nuclear pores. - Have structures such as centrioles, lysosomes, and cilia and flagella that are not typically found in plant cells.
Eukaryotic Cell - Plant cells are also eukaryotic cell. - They have membrane bound organelles. - Larger than animal cells and are typically rectangular or cube shaped. - Have cell wall, large vacuole and plastids, such as chloroplast.-
Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URUJD5 NEXC8
Task : Watch the video and fill in the blanks. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Z9pqST7 2is Bozeman Science Task : worksheets
Scientific Units of Measurement centimeter milimeter micrometer nanometer Cells micrometers Total magnification = Ocular lens/Eyepiece x Objective lens Magnification = Image size/Actual size