Understanding Erectile Dysfunction and Treatment Approaches
Explore the causes, physiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of erectile dysfunction (ED) alongside common medications that can contribute to ED. Learn to distinguish between organic and psychogenic ED, understand treatment goals, and identify counseling points for PDE-5 inhibitors. This comprehensive guide provides insights into managing ED pharmacologically and non-pharmacologically.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Erectile Dysfunction Alesia V. Adams, PharmD Integrated Pharmacotherapy 2b PHR 7601
Learning Objectives Distinguish between organic and psychogenic erectile dysfunction Understand common pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic causes Assess and collect information necessary to address treatment goals Create patient-specific therapeutic plans Identify important counseling points for PDE-5 inhibitors Manage an ED pharmacologic treatment
Background Erectile Dysfunction (also known as impotence) Persistent or recurrent failure to achieve or maintain a penile erection for satisfactory intercourse Persistent 3 months Age: 50 70 yo 52% >70 yo 80% Causes: Concurrent medical conditions: hypertension, arteriosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, or psychiatric disorders Medications
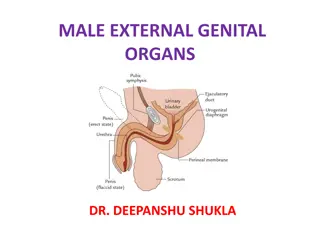
Physiology Flaccid: Arterial to venous blood flow is balanced Erectile: Blood flow increases and compresses the veins, slowing outflow
Physiology Vascular Nervous Hormonal Mental AcH mediated changes to NO, cGMP, cAMP Physical stimulation AcH mediated changes to NO, cGMP, cAMP Emotional stimulation Testosterone mediated changes to NO and cGMP Testosterone mediated enhanced of PDE activity Ability to respond mentally to sexual stimuli
ED Pathophysiology Organic Psychogenic Vascular Nervous Hormonal Mental Conditions that compromise vascular blood flow Conditions that impair nerve conduction to brain or penis Hypogonadism Mental health conditions, Alzheimers, hypothyroidism
Diagnosis Medications Hypogonadism Medical History
Medications Drug Class Drug Class Anticholinergic agents Drugs Drugs antihistamines, antiparkinsonian agents, tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines metoclopramide, phenothiazines Dopamine antagonists Estrogens or drugs with antiandrogenic effects luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists, digoxin, spironolactone, ketoconazole, cimetidine CNS depressants barbiturates, narcotics, benzodiazepines, binging alcohol, anticonvulsants diuretics, peripheral -adrenergic antagonists, or central sympatholytics [methyldopa, clonidine, guanethidine] Agents that decrease penile blood flow 5-alpha reductase inhibitors finasteride, dutasteride
Medical History Age Rule out BPH in men >50 Concurrent medical illnesses Arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease Diabetes Hypertension Lifestyle Changes Drug use Alcohol Smoking
Hypogonadism Signs gynecomastia, small testicles, decreased body hair or beard, and decreased muscle mass Labs two early morning serum testosterone levels on different days, approximately 4 weeks apart
Treatment Non-pharmacologic Pharmacologic Weight loss Exercise Secession of substance use Vacuum Erection Device (VED) Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (PDE-5 inhibitors) Testosterone replacement Intracavernosal injection Intraurethral insert
Pharmacologic treatments
Sildenafil (Viagra) Sildenafil (Viagra) Vardenafil (Levitra) Vardenafil (Levitra) Tadalafil Tadalafil (Cialis) (Cialis) 10-20 mg Avanafil ( Avanafil (Stendra Stendra) ) Dose 25-100 mg 5-20 mg 50-200 mg Onset of action 60 min 25-60 min 30 min 15-30 min Duration 2-4, up to 12 hrs 4-5 hrs 24-36 hrs >6hrs Directions Titrate dose so that erection lasts not more than 1 hour - Better for those who desire spontaneity 5mg daily if on- demand fails Contraindication Nitrates by any route of administration DDI Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors - Renal dose in CrCl <30 in CrCl <30 dose in CrCl <50 Preferred if used with alpha blockers in CrCl <30 - ADE Headache, flush, rhinitis, visual disturbances Headache, flush, rhinitis Headache, flush, rhinitis, back pain Headache, flush, rhinitis 50-80% effective Counseling: - Take on an empty stomach (except tadalafil) - Avoid excessive alcohol intake (orthostatic hypotension) - For best results, use sexual stimulation prior to intercourse
Cardiovascular risk and PDE-5 inhibitors Low Risk Intermediate High Risk Mild or moderate, stable angina Unstable or refractory angina Well controlled HTN NYHA class I or II NYHA class III NYHA class IV MI or stroke within the past 2-8 weeks MI or stroke within the past 2 weeks No MI >8 weeks Safe to initiate PDE-5 Complete cardiovascular workup and stress test PDE-5 contraindicated, defer sexual intercourse
Patient considerations with PDE-5 inhibitors Known cardiovascular disease: Hard work! o Sexual intercourse and orgasm = vigorously climb two flights of stairs = walk 1.5 km If angina develops during sexual intercourse after PDE-5i use o immediately stop and rest for the next 5 to 10 minutes. o if angina does not resolve after 20-30 minutes go to the nearest emergency room
Prostaglandin E1 Alprostadil Alprostadil Intracavernosal Intracavernosal injection injection Intraurethral pellet Intraurethral pellet Dose 2.5-40 mcg intracavernosally 5-10 minutes before intercourse 125-1000 mcg intraurethrally 5-10 minutes before intercourse Onset of action 5-15 min 5-15 min Efficacy 70-90% 40-60% Safety Local effects Avoid use with pregnant partner, local effects Administration requires good aseptic technique and dexterity
Testosterone Supplements MOA: Exogenous testosterone to restore serum ranges to normal Considerations: Time of Onset does not directly address ED; downstream effects may take months Effectiveness only if ED is result of hypogonadism Ease of Administration multiple routes of admin Affordability more convenient forms are more expensive Safety sodium retention (dangerous in CVD)
Non-pharmacologic Vacuum Erection Device Two parts: pump and cylinder Negative pressure draws increased blood flow Tension ring prevents return blood flow Considerations Time of Onset 3-20 minutes (decreases with experience) Effectiveness high satisfaction rate (in intimate relationships) Ease of Administration inconvenient and not discreet, difficult for arthritis Affordability one-time purchase, available OTC Safety few contraindications, symptoms of high pressure, bruising from bands
Key Take-Aways PDE-5 inhibitors preferred if patient can use safely Check dosing and drug interactions Consider CVD history and use of nitrates In patients who fail PDE-5 inhibitors or who cannot manage underlying cause, other options may work
Pharmacist Role Collect a pointed medical history Be aware of drug interactions Counsel on safe use and side effects
Erectile Dysfunction Alesia V. Adams, PharmD Integrated Pharmacotherapy 2b PHR 7602.01