Understanding Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity - LDH Reaction Study
Explore the impact of substrate concentration on lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity in vitro and the factors influencing enzymatic analysis. Learn about the interconversion of lactate and pyruvate catalyzed by LDH, and how pH, inhibitors, and temperature affect enzyme activity. Utilize different substrates and experimental conditions to assess enzyme behavior.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
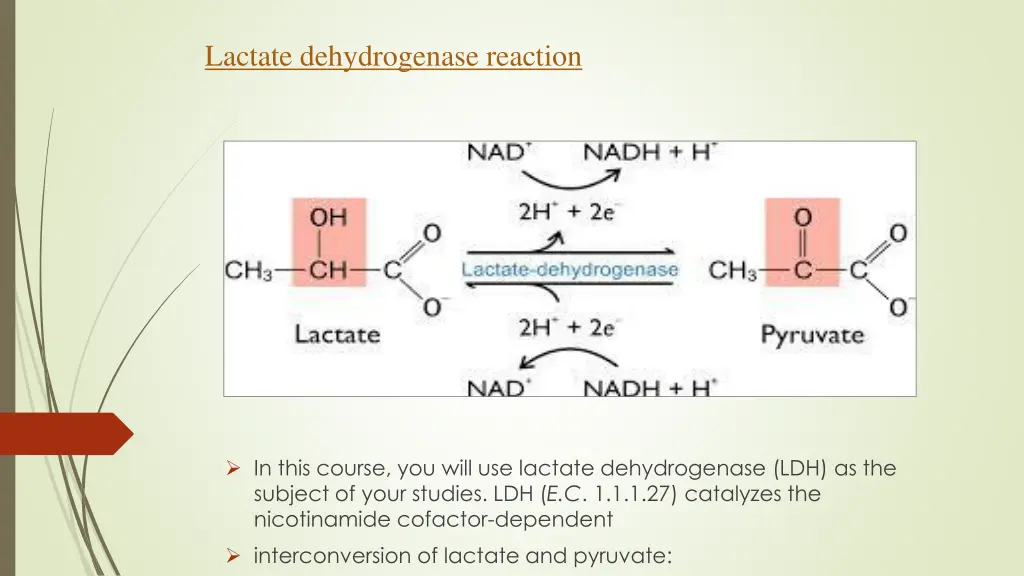
Lactate dehydrogenase reaction In this course, you will use lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as the subject of your studies. LDH (E.C. 1.1.1.27) catalyzes the nicotinamide cofactor-dependent interconversion of lactate and pyruvate:
Enzyme activity is measured in vitro under conditions that often do not closely resemble those in vivo. The objective of measuring enzyme activity is normally to determine the amount of enzyme present under defined conditions, so that activity can be compared between one sample and another, and between one laboratory and another. The factors that affect the activity of an enzyme include substrate concentrations(s), pH, inhibitors and temperature.
The effect of substrate concentration: Reagent pyruvate was ranging from. 0.1 M Tris, pH 7.4, 1.5 mM sodium pyruvate - dilution range 0.05 to 0.5 mM 5 mM NADH (prepared fresh) Enzyme extract For muscle LDH, 0.1 M Tris, pH 7.4 0.1 M lactate stock solution - dilution range5 to 13 mM 5 mM NAD+ (Prepared fresh) Enzyme extract
The effect of substrate concentration: In our experiment, two kinds of substrates have been used one for liver and kidney enzymes and the other for muscle enzyme. These substrates are pyruvate for kidney and liver, Lactate for muscle. The concentration of Lactate was varying from 5 to 13 mM while for pyruvate was ranging from 0.05 to 0.5 mM. Reaction carried out in quartz cuvette of 3 cm light path containing 1.8 ml of 0.1 M Tris, pH 7.4, 0.1 to 1 ml of 1.5 mM sodium pyruvate and 0.1 ml of 5.0 mM NADH (prepared fresh) and 0.1 ml of enzyme extract and the difference in the volume were compensated by adding distilled water. The reaction was started by addition enzyme extract and mixed by inverting the cuvette. The final volume of the reaction mixture was 3 ml. The blank contained all components except NADH. For muscle LDH, reaction carried out in quartz cuvette of 3 cm light path containing 0.2 ml of sodium bicarbonate, 0.4 ml of NAD+, different volumes from lactate stock solution (0.1 M) and the difference in the volume were compensated by adding 0.1 M Tris, pH 7.4, The reaction was started by addition 0.1 ml enzyme extract and mixed by inverting the cuvette. The final volume of the reaction mixture was 3 ml. The blank contained all components except NAD+.
Liver Substrate pyruvate volume ml diS] wate [S] mM Activity 0.1 M Tris, pH 5 mM NADH mlr 7.4 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.05 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 1 - 0.5 Table 8: effect of pyruvate concentration (0.05-0.5mM) on the activity of LDH in liver and kidney and Lactate concentration (5-13 mM) on the activity of muscle LDH.
Liver [S] Activity 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 Table 8: effect of pyruvate concentration (0.05-0.5mM) on the activity of LDH in liver and kidney and Lactate concentration (5-13 mM) on the activity of muscle LDH.
The effect of inhibitors: Urea has been used as a competitive inhibitor that competes with lactate on the active site of LDH and its concentration was 2 M. For LDH in kidney and liver, oxalate was used also as a competitive inhibitor that compete with pyruvate on the active site of LDH in both tissues, oxalate concentration was 0.2 mM [30]. Same enzyme assay except adding of inhibitors were employed here.
Liver Kidney Substrate pyruvate volume ml diS] wate 0.2 mM Oxalate [S] mM 0.1 M Tris, pH 5 mM NADH mlr 7.4 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.05 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 1.8 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 ml 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 1 - 0.5