Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Explore the complexities of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) including its definition, causes, clinical features, and diagnostic methods. Learn about the two main types of IBD, risk factors, and the importance of genetic and immune responses in its development.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
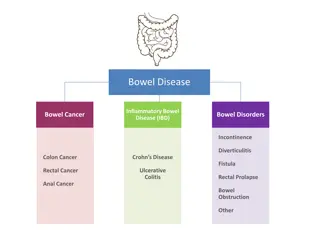
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE BY DR JESSICA MONTEIRO ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DEPT OF PRACTICE OF MEDICINE
OBJECTIVES Defination Causes Clinical features Treatment
. IBD is a chronic condition resulting from inappropriate mucosal immune activation (dysregulated immune response to host intestinal micro flora). It involves chronic inflammation of all part of digestive tract
Types of IBD It involves two types of disorders 1- Ulcerative Colitis- II- Crohn s Disease-
Etiopathogenesis It can occur at any age, frequently in teens in early 30 s, Ulcerative colitis is more common in males & Crohn s among females. Exact etiology of IBD is not known, but it is believed that IBD results from combined effect of Alterations in host response. Intestinal epithelium dysfunction. Mucosal immune response
Factors having important role in IBD 1- Genetic Factor 2- Mucosal Immune response - to bacteria, viruses, or food particles- triggers an inflammatory reaction. 3- Epithelial Defects 4- Microbes
Other risk factors Smoking & use of contraceptive pills increases the risk of Crohn s disease but no such risk for ulcerative colitis. People who live in urban areas and industrialized countries have a higher risk of getting IBD
Clinical Features Symptoms vary according to the location and severity of the disease, as well as the type of disease- Blood in the stool Diarrhea Fatigue Fever Lack of appetite Nausea
Diagnosis In order to diagnose IBD, full medical history of patient is recorded. Tests usually include. -stool culture -X-rays, if a serious complication is suspected -CT Scan -MRI scans, to detect fistulas in the small intestine or anal area
Endoscopy Colonoscopy - to examine the entire colon Flexible sigmoidoscopy - to examine the last section of the colon Upper endoscopy - to examine the food pipe, stomach, and first part of small intestine
Complications Malnutrition with resulting weight loss Colon cancer Fistulas, or ulcers that go through the bowel wall Intestinal rupture, or perforation Bowel obstruction