Understanding Knudsen Diffusion in Chemical Engineering
Explore the concept of Knudsen diffusivity in mass transfer operations, focusing on molecular diffusion, Knudsen diffusion, Knudsen number, and their significance in industrial applications. Learn about the relationship between free mean path and pore diameter, as well as the implications of Knudsen diffusion in gas flow.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
(Prof.) D.K.MEHTA, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT, L.E.COLLEGE-MORBI
TOPIC:- Concept of Knudsen diffusivity, its significance and industrial application SUBJECT:-Mass Transfer Operation-I SUBJECT CODE:-3150501
Molecular diffusion Molecular diffusion is concerned with the movement of individual molecules through a substance by virtue of their thermal energy. The molecules moves in zigzag path and it also collides with another molecules where it changes its direction and magnitude The average distance the molecule travels between collisions is it mean free path.
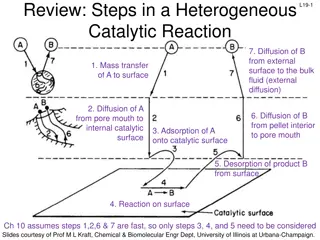
What is Knudsen diffusion If gas diffusion occurs in a very fine pore, particularly at very low pressure, the mean free path of a molecule may be larger than diameter of the passage. Then the collision with the wall becomes more frequent than collision with the other molecules. Then diffusion rate depends on concentration gradient, molecular velocity and diameter of passage. This is known as Knudsen diffusion.
Knudsen Number (Kn):- It is the ratio of free mean path to the diameter of the Pore . = Kn d pore Knudsen Diffusivity(DAA*):- 3 8 u 3 NT = = D * AA M A
But if Kn >1, then d d 8 NT T pore 3 pore 3 = = = 4850 D u d KA pore M M A A If both Knudsen and molecular diffusion exist, then y D N + =1 1 1 1 = + A D D Ae AB KA with B N A For non-cylindrical pores, we estimate = ' 2 D D Ae Ae
Significance The Knudsen number is a good measure of the relative importance of Knudsen diffusion. A Knudsen number much greater than one indicates Knudsen diffusion is important. In practice, Knudsen diffusion applies only to gases because the mean free path for molecules in the liquid state is very small, typically near the diameter of the molecule itself.
Industrial application It becomes important when particle size is below 50 nm. It is occurs commonly for intra-particle transport in a catalyst containing fine pores.