Understanding Refraction of Light in Different Media
Learn about the fascinating phenomenon of light refraction as it changes direction while passing through media of varying optical densities. Explore the concept of index of refraction, speed of light in different mediums, and the relationship between angles of incidence and refraction. Discover how to calculate the index of refraction based on given angles.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
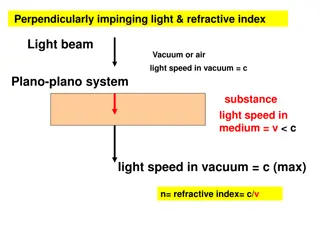
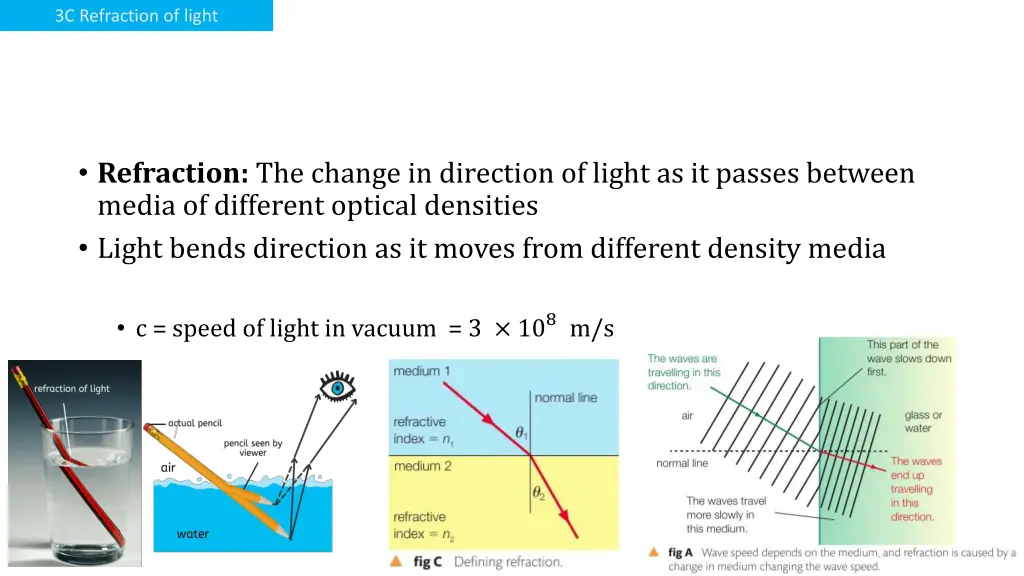
3C Refraction of light Refraction: The change in direction of light as it passes between media of different optical densities Light bends direction as it moves from different density media c = speed of light in vacuum = 3 108m/s
3C Refraction of light Refraction: The change in direction of light as it passes between media of different optical densities because its speed changes. c = speed of light in vacuum = 3 108m/s ?1??? 1= ?2??? 2 Sin of the angle of refraction Index of refraction of 1st medium Index of refraction of 2nd medium
3C Refraction of light Refraction: The change in direction of light as it passes between media of different optical densities Index of refraction: is how much slower the light is in that medium compared to vacuum. ?1??? 1= ?2??? 2 3 108m/s n=????? ?? ??? ? ?? ?????? ????? ?? ??? ? ?? ?????? = ????? ?? ??? ? ?? ?????? *n can t be smaller than 1.00
3C Refraction of light Refraction: The change in direction of light as it passes between media of different optical densities Index of refraction: is how much slower the light is in that medium compared to vacuum. ?1??? 1= ?2??? 2 n=????? ?? ??? ? ?? ?????? ????? ?? ??? ? ?? ??????= ? ?
3C Refraction of light Optical density = Index of refraction: is how much slower the light is in that medium compared to vacuum. ?1??? 1= ?2??? 2 n=????? ?? ??? ? ?? ?????? ????? ?? ??? ? ?? ??????= ? ?
3C Refraction of light There s a linear relation between ??? 1 and ??? 2 ? ? ???????? ??????1 and ????2 yields the index of refraction https://chart-studio.plotly.com/~timtjtim/51.embed
3C Refraction of light A light ray fell from air on the water surface in an incidence angle of (60 ) and its refraction angle in water was (40.5 ), find the index of refraction of water?
3C Refraction of light Assumptions Assumptions Diffraction angle is measured from the normal line, not the horizontal surface The light rays are assumed to be parallel and with the same frequency Air has index of refraction = 1 Mediums are truly transparent
3C Refraction of light Assumptions: how do we reduce Assumptions: how do we reduce measurement errors in practical measurement errors in practical Use accurate instruments Use a consistent coherent light source (example, a laser) Repeat measurements several times Reduce vibration Measure in a dark room
3C Refraction of light Light dispersion through a prism ?1??? 1= ?2??? 2