Understanding Shortest Path Algorithms: Dijkstra, Bellman-Ford, Floyd-Warshall
Discover the power of Dijkstra's, Bellman-Ford, and Floyd-Warshall algorithms for finding the shortest paths in graphs. Learn how each algorithm uniquely approaches path-finding and their applications. Explore their differences and advantages to optimize route planning and graph analysis.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SHORTEST PATH ALGORITHMS Dijkstra s Algorithm Bellman-Ford Algorithm Floyd-Warshall Algorithm Johnson s Algorithm
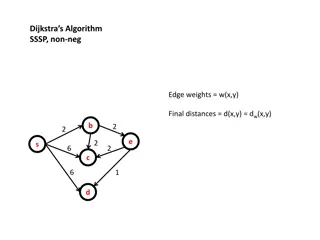
Dijkstras Algorithm Dijkstra s Algorithm stands out from the rest due to its ability to find the shortest path from one node to every other node within the same graph data structure. This means, that rather than just finding the shortest path from the starting node to another specific node, the algorithm works to find the shortest path to every single reachable node provided the graph doesn t change.
Dijkstras Algorithm The algorithm runs until all of the reachable nodes have been visited. Therefore, you would only need to run Dijkstra s algorithm once, and save the results to be used again and again without re-running the algorithm again, unless the graph data structure changed in any way. In the case of a change in the graph, you would need to rerun the graph to ensure you have the most updated shortest paths for your data structure.
Bellman-Ford Algorithm Similar to Dijkstra s algorithm, the Bellman-Ford algorithm works to find the shortest path between a given node and all other nodes in the graph. Though it is slower than the former, Bellman-Ford makes up for its a disadvantage with its versatility. Unlike Dijkstra s algorithm, Bellman-Ford is capable of handling graphs in which some of the edge weights are negative.
Bellman-Ford Algorithm It s important to note that if there is a negative cycle in which the edges sum to a negative value in the graph, then there is no shortest or cheapest path. Meaning the algorithm is prevented from being able to find the correct route since it terminates on a negative cycle. Bellman-Ford is able to detect negative cycles and report on their existence.
Floyd-Warshall Algorithm The Floyd-Warshall stands out in that unlike the previous two algorithms it is not a single-source algorithm. Meaning, it calculates the shortest distance between every pair of nodes in the graph, rather than only calculating from a single node. It works by breaking the main problem into smaller ones, then combines the answers to solve the main shortest path issue.
Floyd-Warshall Algorithm Floyd-Warshall is extremely useful when it comes to generating routes for multi-stop trips as it calculates the shortest path between all the relevant nodes. For this reason, many route planning software will utilize this algorithm as it will provide you with the most optimized route from any given location. Therefore, no matter where you currently are, Floyd- Warshall will determine the fastest way to get to any other node on the graph.
Johnsons Algorithm Johnson s algorithm works best with sparse graphs one with fewer edges, as it s runtime depends on the number of edges. So, the fewer edges, the faster it will generate a route. This algorithm varies from the rest as it relies on two other algorithms to determine the shortest path. First, it uses Bellman-Ford to detect negative cycles and eliminate any negative edges. Then, with this new graph, it relies on Dijkstra s algorithm to calculate the shortest paths in the original graph that was inputted.
Conclusion More often than not, the best algorithm to use won t be left up to you to decide, rather it will be dependant upon the type of graph you are using and the shortest path problem that is being solved. For example, for problems with negative weight edges, you would turn to Bellman-Ford, whereas for sparse graphs with no negative edges you would turn to Dijsktra s algorithm.
Conclusion When it comes down to it, many aspects of these algorithms are the same, however, when you look at performance and use, that s where the differences come to light. Therefore, rather than asking which algorithm is the best, you should consider which is the right one for the type of graph you are operating on and shortest path problem you are trying to solve.
Dijktras shortest path Algorithm
Dijktras algorithm between 2 nodes
Dijkstras algorithm based on Euclidean distance