Understanding the Immune System and Pathogen Defense
Explore the fascinating world of the immune system, including how it identifies and fights pathogens, the role of antigens and antibodies, and the organs involved. Learn about immunity, leukocytes, and the different types of pathogens that can invade the body.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bodies defense against pathogens Immune System recognizes the identity of foreign substances Antigens are found on the cells of all organisms and your body is able to identify your own cells and tell when a foreign cell has entered the system Foreign antigens trigger a reponce to attack the pathogen
Immunity - an accumulation of specific antibodies enabling an individual to resist specific diseases.
Unlike other body systems, The Immune System is NOT contained within a single set of organs or vessels, Action depends on structures from lymphatic, cardiovascular, and Integumentary systems Works primarily through antigen-antibody reaction
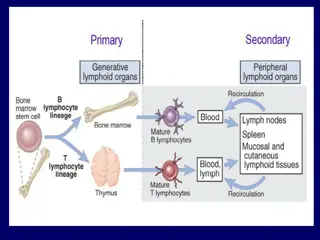
Organs of the Immune System
Pathogens- Foreign invaders that enter the immune system and cause an immune response. Also known as Antigens Bacteria Viruses Fungi Protists Streptococcus Bacteria Rhinovirus See full size image Amoebic Dysentery
Pathogens have tags surrounding them called antigens that indicate that they are invaders to the body Antigens Bacteria
Antigen vs. Antibody Antigen - any substance that the body regards as foreign (virus, bacterium, toxin) Antibody - a disease fighting protein developed by the body in response to the presence of an antigen Antigen-antibody reaction or immune reaction
Leukocytes- Another name for white blood cells, there are two general classes of leukocytes Phagocytes (macrophage )- phagocytic (surrounds and engulfs) protects body by ingesting invading cells Lymphocytes Cells that produce specific antibodies against a foreign pathogen
T cells or T Lymphocytes mature in thymus gland Cell mediated immunity B cells or B Lymphocytes mature in bone marrow antibody-mediated immunity
Any change other than injury that disrupts the normal functioning of the body. Some diseases are inherited, some are caused by environmental factors, and other are caused by agents such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi. FAILURE IN HOMEOSTASIS
The human body provides the right conditions for pathogens. We provide them with the right temperature, watery environment nutrients
Break down tissue in infected organs Release toxins into the body Live and feed inside the infected organism Destroy host cells
Bodily fluids Break in the skin Food Water Air Insect bites (Insects are vectors) Vector-Animal that carried a disease causing organism
Skin Barrier Provides and acidic environment
Tears Saliva Sweat All contain Lysozymes which destroy bacteria and viruses
Second Line of Defense The Immune System- bodies primary defense against pathogens Pathogens are disease causing microbes
What do you think happens to the number of white blood cells in the area?
Bacteria and Viruses have a certain temperature range in which they can function. Raising the temperature from 98.6 to 100 or greater will cause the bacteria and the viruses to die.
Inhibits the synthesis of viral proteins in infected cells and will help block viral replication
Immune System response to a harmless substance Food, Pollen, Bee Stings Immune System releases histamines, which cause rash, swelling, tears, runny nose and watery eyes Antihistamines reduce these symptoms
Contain antigens from another person Immune system does not recognize it as self and will attack it (Rejection) Immunosupresent Drugs are taken to weaken the immune system of a person receiving a transplanted organ
Antigens stimulate development of antibodies that are unable to distinguish antigens of internal cells. Body makes antibodies and T cells against itself and attacks own tissues. Multisystemic involvement. Myasthenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis
An autoimmune reaction attacks the insulin producing cells of the pancreas
An autoimmune disease of the nervous system that results from the destruction of the myelin sheath