Understanding UML - A Comprehensive Overview
Explore the world of Universal Modeling Language (UML) and its significance in software development. Learn about the different types of diagrams, UML hierarchy, notation, and more. Dive into the details of UML notations, inheritance, association, states, interfaces, and interaction diagrams to enhance your understanding of UML concepts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
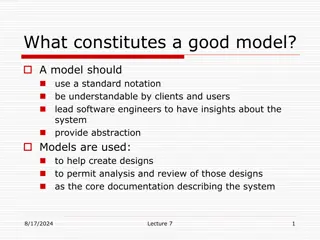
What is UML? Universal Modeling Language - Created during the OO ascendance - An attempt to have a consistent way to diagram out - Architecture - Design - Requirements In the case of Requirements, UML was heavily touted as the way to show Use Cases
Types of diagrams Class diagram Object diagram Use case diagram Sequence diagram Collaboration diagram Activity diagram Statechart diagram Deployment diagram Component diagram We ll look at Use Case Diagrams for now
UML Hierarchy UML Structural Behavioural Use Case State Activity Class Component Deployment Object Package Interaction Structure Timing Communication Sequence
Notation: Class & Object Underline indicates object Classes Objects Student Visibility +: public -: Private #: Protected Name Student +name: String #ID: int -SS:String +Create() +Display() +Update() -Delete() +name: String #ID: int -SS:String +Create() +Display() +Update() -Delete() Responsibilities - Manage Student Record Attributes Methods Optional information What s the difference between a class and an object?
Notation: Inheritance and Association Passengers Child Parent 0..* Generalization (increasing) Aeroplane Association Inheritance
Notation: States ATM Transaction Idle Waiting for Selection Insert Card Initial State Initial State Normal Exit Waiting for PIN Confirmation Final State Abnormal Exit (PIN Failure) Terminal State
Notations Interfaces: A circle with a name
Interaction diagrams Communications between objects
The classes Client Sequence Diagrams Client object Supplier PerformResponsibility() PerformAnotherResponsibility() Supplier object Object Lifeline : Client : Supplier Reflexive message (Message to self) 1. PerformResponsibility 1.1. PerformAnotherResponsibility Message Hierarchical message numbering Focus of Control (Activation) Sequence diagrams illustrate how objects interact with each other dynamically
Components of Use Cases Intent - To show the software from the perspective of the user The actor The use cases
The shift in focus Once the gold standard, UML has reduced in usage for a few reasons: - Complexity in notation - Time to create - Lack of clarity So why talk about it? - Some parts are still very relevant - Sequence diagrams, Swim Lanes, - You may run into this in interviews or on the job (UML has been around, and legacy lives on!)
References https://www.tutorialspoint.com/uml/uml_basic_notations.htm http://empirical-software.engineering/assets/pdf/fse14-sketches-slides.pdf