Wireless VOD Based on Popularity
The dynamics of Video On Demand (VOD) services, this content delves into the concept of popularity in wireless networks. It covers the current architecture, network crowdsourcing, system models, and the significance of introducing popularity in managing bandwidth allocation for different kinds of videos. The content includes classification, definition, and strategies for segment popularity, providing a comprehensive overview of optimizing VOD services based on user preferences.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Wireless VODbased on popularity Liu Siyi 5120309667
Catalogue Introduction Current architecture Popularity
Introduction What is VOD? Video On Demand
Introduction Why study VOD?
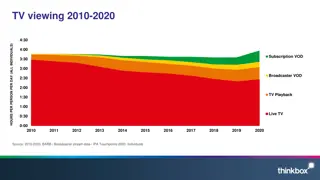
Introduction Cable VOD period broadcasting Cable network, stable bandwidth
Introduction Wireless VOD Wireless network, unstable bandwidth
Current architecture Network Crowdsourcing Architecture
Current architecture System model
Popularity Why introduce popularity? 80% of the requests concentrate on 20% videos The other 20% of the requests scatter among the other 80% videos popularity popular unpopular
Popularity Classification Video popularity Segment popularity
Popularity Definition M servers, N videos, For server i and video j, Wi,j, is the weight of j to i. Thus, the popularity of video k is: 1 M M W , i k = ( ) P k N = 1 i W , i j = 1 j
Popularity Video popularity Set threshold for different kinds of videos Reserve different amount of bandwidth Use the idle bandwidth
Popularity Segment popularity
Flow-process diagram New request Calculate video popularity Meet the threshold reject Yes No Distribute bandwidth Enough bandwidth reject No Yes Calculate segment popularity Distribute time slot