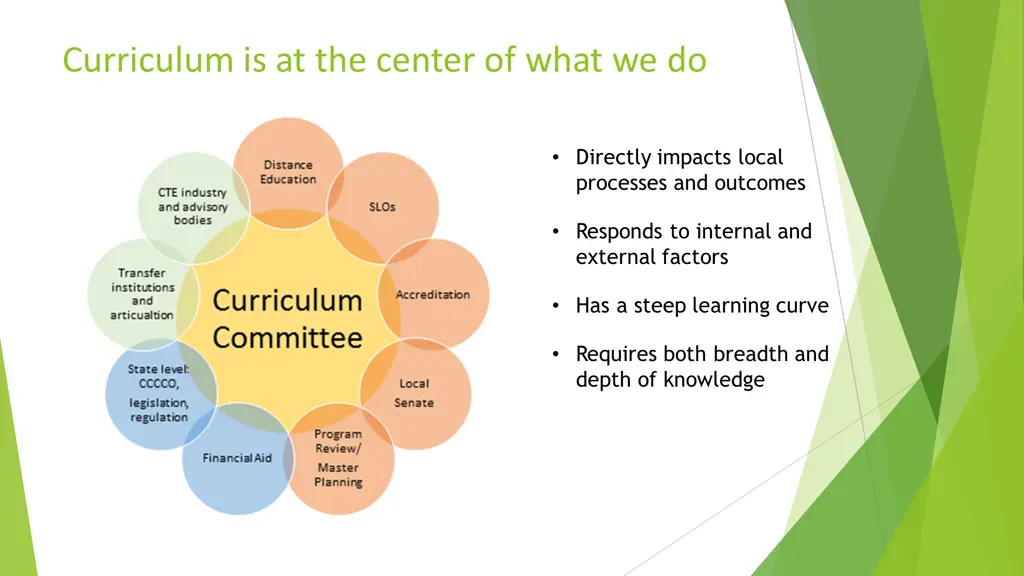
Curriculum is at the center of what we do
Curriculum plays a central role in educational processes and outcomes, responding to internal and external factors with a steep learning curve. AB 1725 empowers Academic Senates with purview over curriculum. The 10+1 outlines key areas, including prerequisites, governance, and accreditation. Courses and programs vary, from credit to non-credit, offering diverse learning opportunities. Detailed requirements govern courses, ensuring quality and alignment with educational goals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Curriculum is at the center of what we do Directly impacts local processes and outcomes Responds to internal and external factors Has a steep learning curve Requires both breadth and depth of knowledge
Curriculum Is Part of Faculty Purview Through the Senate AB 1725 (Vasconcellos, 1988) provided the Academic Senate at each college with specific areas of purview, either in terms of primary reliance or mutual agreement in what is know as the 10+1 . Curriculum is the first of the 10+1. This also established that approval of curriculum at the local level is the responsibility of the Academic Senate or a subcommittee of the Academic Senate, which would be the curriculum committee or other group comprised primarily of faculty, which has been designated as the approving body. It is the duty of the Senate to address, either directly or through its designated committees, all matters pertaining to the educational well-being of the college, to develop and establish [faculty] positions on all such matters and to inform all relevant constituencies, inside and outside the college, of these positions.
The 10+1 1. Curriculum, including establishing prerequisites and placing courses within disciplines; 2. Degree and certificate requirements; 3. Grading policies; 4. Educational program development; 5. Standards or policies regarding student preparation and success; 6. District and college governance structures, as related to faculty roles; 7. Faculty roles and involvement in accreditation processes, including self study and annual reports; 8. Policies for faculty professional development activities; 9. Processes for program review; 10. Processes for institutional planning and budget development; and 11. Other academic and professional matters as mutually agreed upon between the Governing Board and the Academic Senate.
Types of Courses and Programs Credit Noncredit Courses Degree applicable Non-degree applicable Courses Noncredit: no credit awarded for courses in 10 categories but approved by CO and receives apportionment Programs Associate Degrees (AA, AS) Associate Degrees for Transfer (AA-T, AS-T) Certificates of Achievement 8 to less than 16 semester units 16 or more semester units Locally Approved Certificates <16 units, CO approval optional Programs Certificate of Completion (CDCP) Certificate of Competency (CDCP) Adult High School Diploma Noncredit Apprenticeship Program Locally Approved Certificates (not CO approved)
Requirements for Courses Course Number and Title Catalog Description Prerequisites, Corequisites, Advisories Units Total Contact Hours Total Number of Hours in Each Instructional Category Outside of Class Hours Course Content Objectives/Outcomes Instructional Methods Grading criteria (letter grade, P/NP) Methods of Assessment Reading, Writing, and Outside of Class Assignments Repeatability Options Justification of Need CCCCO Data Elements Discipline Assignment(s) Articulation/Transfer Information Textbooks SLOs
Credit Program Requirements Associate Degrees Minimum of 60 units At least 18 units in a major or area of emphasis Can use any GE pattern, local, CSU GE-B, IGETC. Associate Degrees for Transfer (ADTs) Minimum 60 units, maximum 60 units At least 18 units in a major or area of emphasis GE pattern limited to CSU GE or IGETC patterns Certificates of Achievement Minimum of 8 units to submit for control number and to be able to be transcribed *NOTE: 16 units required for program to qualify for financial aid.
The pressure is on Curriculum streamlining means more responsibility on colleges to ensure quality and compliance in curriculum Annual Certification allows colleges to certify that curriculum is developed and approved in accordance with Ed Code, Title 5 and PCAH. This expedites the approval process for courses and certain program submissions. Review is still done for the following: New and revised ADTs New CTE Certificates of Achievement New CTE AS/AA Degree New and revised CDCP Noncredit (short term vocational) Colleges must still maintain supporting documents for all awards
Elements of Approval processes: The District Governing Board approves the course or program The Regional Consortium recommends the program (only for programs with an occupational goal) The Chancellor s Office chapters the course or program and a control number is issued *A course or program may only be published once a control number is received. Development Criteria Appropriateness to Mission Need Curriculum Standards Adequate Resources Compliance
Compliance and Quality Matter Approval Apportionment Articulation Accreditation Access
Tech review vs Content review Curriculum review takes two distinct forms: Technical review ensures complete data, compliance, and consistency Subcommittee curriculum chair(s), originator (if needed), others involved with data and compliance needs Content review is done by discipline faculty (prior to technical review), but the curriculum committee needs to look at content too Assignment of a discipline, min qualifications Avoiding duplication of existing curriculum Appropriateness to college mission Integration of elements of COR (content, objectives, assignments, etc.)
Curriculum Systems CurriQunet Login is not required to access course outlines. All work on courses and programs begins in this system. Launched proposals must be at the tech review level by the Wednesday before the next meeting to be included on the next meetings agenda. California Community Colleges Curriculum Inventory (COCI) All courses and programs are uploaded to COCI Control number required to publish new proposals Banner Allows courses to be scheduled and programs to be awarded DegreeWorks Web-based planning tool shows progress toward program completion Nuventive All outcomes (SLO/PLO/SAO/ILO) and program review Program Pathways Mapper Learning and Career Pathways shows when courses are offered to assist with educational plan.