Comparing PI vs. PI in HIV Treatment Studies
Explore the comparison of different protease inhibitors (PI) in HIV treatment studies, including atazanavir (ATV) vs. ritonavir-boosted ATV, lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) monotherapy vs. combined with zidovudine/lamivudine, and more. Dive into Study BMS 089 focusing on ATV vs. ATV/r combination therapy with 3TC and d4T. Analyze baseline characteristics, patient disposition, response to treatment at week 48, and treatment-emergent resistance findings. Stay informed on the latest advancements in HIV treatment strategies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
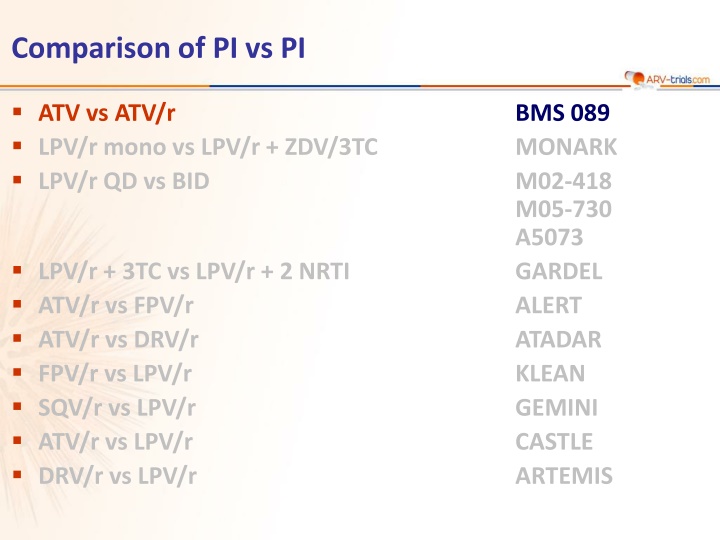
Comparison of PI vs PI ATV vs ATV/r LPV/r mono vs LPV/r + ZDV/3TC LPV/r QD vs BID BMS 089 MONARK M02-418 M05-730 A5073 GARDEL ALERT ATADAR KLEAN GEMINI CASTLE ARTEMIS LPV/r + 3TC vs LPV/r + 2 NRTI ATV/r vs FPV/r ATV/r vs DRV/r FPV/r vs LPV/r SQV/r vs LPV/r ATV/r vs LPV/r DRV/r vs LPV/r
Study BMS 089: ATV vs ATV/r QD, in combination with 3TC + d4T XR QD Design Randomisation* 1 : 1 Open-label W48 ATV/r 300/100 mg QD 200 adults N = 95 ARV-na ve or < 30 days of prior NRTI or < 7 days of prior NNRTI or PI HIV RNA > 2,000 c/mL Any CD4 cell count 3TC + d4T XR QD ATV 400 mg BID N = 105 3TC + d4T XR QD *Randomisation was stratified on HIV RNA < or > 100,000 c/mL Objective Non inferiority of ATV/r 300/100 vs ATV 400 at W48: % HIV RNA < 400 c/mL, ITT, TLOVR algorithm (lower margin of the 95% CI for the difference = -10%, 80% power) Malan DR. JAIDS 2008;47:161-7 BMS 089
Study BMS 089: ATV vs ATV/r QD, in combination with 3TC + d4T XR QD Baseline characteristics and patient disposition ATV/r ATV 400 mg 300/100 mg Randomized, N 95 105 Treated eligible patients, N 95 104 Median age, years 35 34 Female 27% 30% White/Black/Other 53% / 26% / 21% 57% / 26% / 17% HIV RNA (log10c/mL), median HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL 4.8 5.1 42% 52% CD4 cell count (/mm3), median 201 194 CD4 < 200/mm3 48% 52% Hepatitis B and/or C positive 18% 19% Discontinuation before W48 12% 10% Malan DR. JAIDS 2008;47:161-7 BMS 089
Study BMS 089: ATV vs ATV/r QD, in combination with 3TC + d4T XR QD Response to treatment at week 48 (ITT, TLOVR) ATV/r (N = 95) Primary endpoint ATV (N = 105) % 100 HIV RNA < 400 c/mL HIV RNA < 50 c/mL HIV RNA < 50 c/mL 87 86 85 82 80 75 70 63 58 60 40 20 N = 46 50 49 55 0 All patients 95% CI for the difference = - 7; 17 Baseline HIV RNA < 100,000 c/mL Baseline HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL 95% CI for the difference = - 8.2; 11.1 Median CD4 increase at W48: 174/mm3(ATV/r) vs 213/mm3(ATV) Malan DR. JAIDS 2008;47:161-7 BMS 089
Study BMS 089: ATV vs ATV/r QD, in combination with 3TC + d4T XR QD Treatment-emergent resistance Genotypic and phenotypic resistance in patients with virologic failure through W48 ATV/r N = 3 N = 2 ATV N = 10 N = 8 HIV RNA > 400 c/mL Resistance testing PI major substitutions 0 1 # I50L, N88S I50I/L 0 2 PI minor substitutions * 1 4 ATV phenotype: FC > 2.2 0 1 (FC = 26) # M184V 1 7 # Same patient; * Among 20I/T, 33F, 34Q, 36V, 64V, 71V, 73S, 74A, 83D Malan DR. JAIDS 2008;47:161-7 BMS 089
Study BMS 089: ATV vs ATV/r QD, in combination with 3TC + d4T XR QD Safety ATV/r ATV Serious adverse event 15% 16% Discontinuation for adverse event 8% < 1% Grade 2 to 4 treatment-related adverse event 43% 34% Jaundice 3% < 1% Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormality Total bilirubin > 2.5 x ULN 59% 20% ALT > 5 x ULN 6% 3% AST > 5 x ULN 3% 3% Total cholesterol > 300 mg/dL 1% < 1% Triglycerides > 751 mg/dL 2% < 1% Upward shift of > 1 NCEP category at W48 for ATV/r vs ATV: total cholesterol: 16% vs 11% LDL-cholesterol: 46% vs 48% triglycerides: 30% vs 18% Malan DR. JAIDS 2008;47:161-7 BMS 089
Study BMS 089: ATV vs ATV/r QD, in combination with 3TC + d4T XR QD Summary - Conclusion For first-line antiretroviral therapy, ATV/r 300/100 mg QD was virologically non inferior to ATV 400 mg QD, when combined with 3TC and d4T XR QD Response rate at an HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48 was 25% less in patients with baseline HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL as compared with baseline HIV RNA < 100,000 c/mL Virologic failure occurred more frequently in the ATV group (9.5% vs 3.2%) with emergence of major atazanavir-associated mutations in 3/8 tested patients in the ATV group Results (HIV RNA < 50 c/mL at W48, virologic failure rate, resistance data) suggest ATV/r is more potent than ATV Discontinuation due to treatment-related adverse event occurred more frequently in the ATV/r group Increases in total cholesterol and triglycerides were greater in the ATV/r group Possible impact of stavudine on lipid increases Limitation: small size of the study Malan DR. JAIDS 2008;47:161-7 BMS 089
















