Development of Internal Dose Calculation Code: Features and Background
Background information on the development of Internal Dose Calculation Code (IDCC) at Japan Atomic Energy Agency, focusing on regulatory standards, revision of Japanese standards, features of IDCC, and future plans.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Development of Internal Dose Calculation Code (IDCC) Kentaro MANABE Japan Atomic Energy Agency RASSC 57 meeting, Dec. 2024 1
Contents Background Features of Internal Dose Calculation Code (IDCC) Two main functions Graphical user interface Extensibility of dosimetric models and data Current Status and Future Plans of IDCC Development Summary 2
Background The existing Japanese regulatory standards against internal exposures Effective dose coefficient for workers (mSv/Bq) Kind of radioisotope Concentration limit (Bq/cm3) Air in workplace 1 104 Exhaust from facility 7 101 Drainage from facility Nuclide Chemical form Inhalation Ingestion 1.8 10 12 3H Elemental gas 1.8 10 8 1.8 10 8 8 10 1 5 10 3 6 101 3H Water 4.1 10 8 4.2 10 8 5 10 1 3 10 3 2 101 3H Organically bound 999 nuclides of 91 elements Used for dose estimation from individual monitoring Limit to protect workers Limit to protect members of the public Concentration limits are calculated using effective dose coefficient, e( ), and reference values of ventilation rate and water intake. Air in workplace: e( ) for workers are used. Exhaust and drainage from facility: age-dependent e( ) for members of the public are used. The existing limits are based on e( ) from 1990 Recommendations. 3
Revision of the Japanese Regulatory Standards The Nuclear Regulation Authority, Japan (NRA) is considering to introduce the 2007 Recommendations into the regulatory system. Incorporation of e( ) from 2007 Recommendations is necessary. Problems The current Japanese standards include short-lived (T1/2<10 min) nuclides, whose e( ) are not provided by the ICRP. Intake estimation tool (software) is required for dose assessment from individual monitoring. There is a need for explanation of the influence of Japanese specific parameters or conditions on doses. Difference in physique between Japanese and ICRP reference man. Japanese specific biokinetics (e.g. uptake ratio of iodine to the thyroid). It is important to establish a technical basis for internal dose estimation. JAEA has been developing an internal dosimetry code as a project commissioned by NRA. 4
Contents Background Features of Internal Dose Calculation Code (IDCC) Functions Graphical user interface Editability of dosimetric models and data Current Status and Future Plans of IDCC Development Summary 5
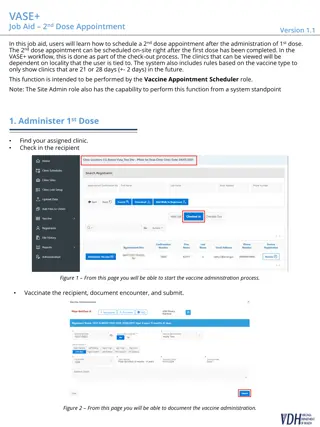
Features of IDCC IDCC allows to: Calculate e( ) using a methodology and dosimetric Models and Data in line with the 2007 Recommendations, Estimate intake of nuclides and resulted doses from individual monitoring, Users can operate IDCC through a Graphical User Interface (GUI). Users can edit dosimetric models and data in calculation of e( ) and estimation of intakes. Screenshot of GUI of IDCC 6
Function Calculating Effective Dose Coefficient, e() Set intake conditions Nuclide Intake route Chemical form View calculation results e( ) Time-dependent change of activity in the body User (GUI) Start End Refer models and data Nuclide data Biokinetic model Radiation absorption data Calculate Activity distribution Absorbed dose Dose coefficient, e( ) IDCC Models and Data Dosimetric models and data IDCC carries out very complicated calculation each time. For details of the calculation process, please refer the material of RASSC 56, R.6.1 presented by Dr. Paquet. 7
Function Estimating Intake from Individual Monitoring Input monitoring results Intake conditions Monitoring method Evaluated activity View results User (GUI) Estimated intake Effective dose evaluated as product of intake and e( ) Start End Refer models and data Nuclide data Biokinetic model Radiation absorption data Calculate Estimate intake Maximum likelihood estimation with a(t) and monitoring results Time-dependent change of activity in the body, a(t) e( ) IDCC Models and Data Dosimetric models and data IDCC can be applied to dose estimation from individual monitoring in line with the 2007 Recommendations. 8
Graphical User Interface (GUI) The GUI allows intuitive operation. 10
Editability of Data and Models Directory Structure of IDCC Files of Models and Data are Isolated from application file, Written in XML or plain text. User can edit and/or replace the files. Models and Data referred in calculation Java application Example of XML Data: Systemic Biokinetic Model XML style XML data can be edited using Excel. 11
Contents Background Features of Internal Dose Calculation Code (IDCC) Functions Graphical user interface Editability of dosimetric models and data Current Status and Future Plans of IDCC Development Summary 12
Current Status and Future Plans of IDCC Development All models and data essential for calculating e( ) for occupational intakes have been incorporated. Nuclear Decay Data (ICRP107) Biokinetic model (ICRP130, 134, 137, 141, 151) Absorption Fraction Data for Internal Radiation (ICRP133) Verification of the functions was performed as follows: We plan to incorporate age-dependent models and data for members of the public. 13
Contents Background Features of Internal Dose Calculation Code (IDCC) Functions Graphical user interface Editability of dosimetric models and data Current Status and Future Plans of IDCC Development Summary 14
Summary IDCC is being developed as a technical basis for implementation of ICRP 2007 Recommendations into Japanese regulatory standards. IDCC can calculate e( ) and estimate intake of radionuclides from monitoring measurements, using methodology and Models and Data in line with ICRP 2007 Recommendations. For occupational intakes, incorporation of models and data is completed. Age-dependent models and data will be incorporated. Fund This project is funded by the Nuclear Regulation Authority, Japan. Contact manabe.kentaro@jaea.go.jp 15