Fetal Abdominal Anomalies and Malformations
Explore the various fetal abdominal anomalies and malformations such as duodenal atresia, ascites, echogenic bowel, and situs inversus. Learn about the causes, associated conditions, and implications for prognosis and treatment. Images and descriptions provide insights into conditions affecting the fetal abdomen during development.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fetal Abdominal Anomalies DMS 443 By: Lauren Sanchez
Normal Rotation of midgut (6-11 weeks) Normal organs of the abdomen Liver Biliary system Spleen stomach Kidneys Colon Stomach
Malformations of the midgut Umbilical Hernia Meckel s Diverticulum Normal intestines go back into the abdomen Umbilicus doesn t close properly Acquired or congenital Most Common malformation of the midgut Outpouching of the small intestine Failure of absorption of the vitelline duct
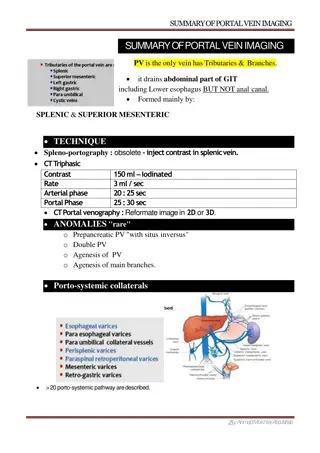
Duodenal Atresia Absence or complete closure of a portion of the lumen of the duodenum Associated: Trisomy 21 polyhydramnios Sono: Two cystic structures Double Bubble
Ascites Fluid in the fetal abdomen Prognosis: poor in nonimmune hydrops Cause: Bowel perforation Bladder rupture idiopathic bowel perforation (e.g. meconium peritonitis) ovarian cyst rupture intrauterine infections hydrometrocolpos
Echogenic Bowel Fetal bowel displays an echogenicity or brightness equal to or greater than that of surrounding fetal bone Seen in 2nd trimester Cause: Decreased water content Alterations to meconium 3 Grades: Grade 1: mildly echogenic and diffuse Grade 2: Moderately echogenic and focal Grade 3:Very echogenic, similar to bone structures
Situs Inversus Total situs inversus right-side heart axis transposition of liver stomach and spleen left-side gallbladder Partial situs inversus right-side stomach left-side liver
Limb Body Wall Syndrome Opening of the anterior body wall Congenital Associated with: Amniotic band syndrome anencephaly Encephalocele Facial cleft Left side of the body wall defects are 3X more common that the right side Prognosis: poor
Omphalocele Organs stick out from belly button with a thin layer of membrane covering them Usually have other complications heart defects and neural tube defects Sono: ascites, echogenic
Gastroschisis Paraumbilical defect Usually found to the right of umbilicus AFP levels will significantly be higher Detected after 12 weeks Floating membranes without covering membrane Not genetically inherited No association with other anomalies
Amniotic Band Syndrome Rupture of the amnion Sticky chorion Leads to Amputations Can include anomalies Limbs Face Thorax Abdominal wall Peronium
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome Rare disorder Common with Omphalocele Macroglossia Visceromegaly Characterized by Macrosomia Macroglossia Embryonic tumors Ear creases Sono Omphalocele Growth acceleration Macroglossia In 3rd trimester polyhydramnios
Bladder and Cloacal Exstrophy Bladder becomes exposed to lower abdomen Common with: Omphalocele Inguinal hernia Undescended testes Anal problems Exstrophy of bladder and rectum Imperforate anus Spinal defects Many abdominal structures are exposed
References Weerakkody, Yuranga. (n.d). Physiological gut herniation. Retrieved from https://radiopaedia.org/articles/physiological-gut-herniation?lang=us Facts about Omphalocele. (n.d). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/omphalocele.html Cloacal Exstrophy. (n.d). Retrieved from https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/cloacal-exstrophy Meckel's Diverticulum. (n.d). Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14738-meckels-diverticulum Limb-body wall complex. (n.d). GARD. Retrieved February 6, 2020, from https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/3251/limb-body-wall-complex