IEEE 802.3 Criteria for Standards Development
The IEEE 802.3 Criteria for Standards Development outlines the requirements for developing standards within the IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee. This includes criteria such as project process requirements, Managed Objects, Five Criteria (5C), coexistence assurance for wireless projects, broad market potential considerations, and compatibility with existing IEEE standards. The document addresses key aspects like managed objects development, coexistence assurance, market potential assessment, and standard compliance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
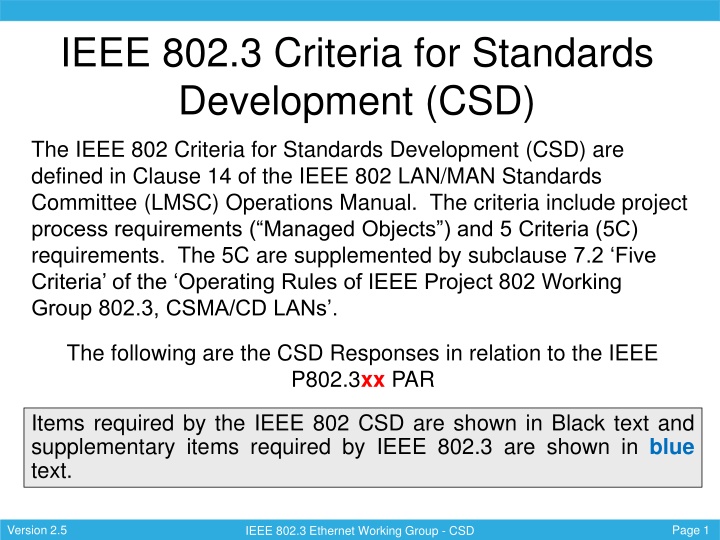
IEEE 802.3 Criteria for Standards Development (CSD) The IEEE 802 Criteria for Standards Development (CSD) are defined in Clause 14 of the IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee (LMSC) Operations Manual. The criteria include project process requirements ( Managed Objects ) and 5 Criteria (5C) requirements. The 5C are supplemented by subclause 7.2 Five Criteria of the Operating Rules of IEEE Project 802 Working Group 802.3, CSMA/CD LANs . The following are the CSD Responses in relation to the IEEE P802.3xx PAR Items required by the IEEE 802 CSD are shown in Black text and supplementary items required by IEEE 802.3 are shown in blue text. Version 2.5 Page 1 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD
Managed Objects Describe the plan for developing a definition of managed objects. The plan shall specify one of the following: a) The definitions will be part of this project. b) The definitions will be part of a different project and provide the plan for that project or anticipated future project. c) The definitions will not be developed and explain why such definitions are not needed. The definition of protocol independent managed objects, to be included in Clause 30 of IEEE Std 802.3, will be part of this project. Version 2.5 Page 2 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD
Coexistence A WG proposing a wireless project shall demonstrate coexistence through the preparation of a Coexistence Assurance (CA) document unless it is not applicable. a) Will the WG create a CA document as part of the WG balloting process as described in Clause 13? b) If not, explain why the CA document is not applicable A CA document is not applicable because the proposed project is not a wireless project. Version 2.5 Page 3 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD
Broad Market Potential Each proposed IEEE 802 LMSC standard shall have broad market potential. At a minimum, address the following areas: a) Broad sets of applicability. b) Multiple vendors and numerous users. Broad Sets of Applications: Recent automotive architectural changes (zonal or central architecture) require automotive Ethernet rates in excess of 10Gb/s. High-performance cameras, CPU-to-CPU links, redundant links, sensor aggregation and flight data recorder systems require minimum data rates of 25 Gb/s. Multiple vendors and numerous users: At the Call for Interest, 73 individuals from 44 organizations indicated they would support this project. These included automotive OEMS, automotive Tier 1, silicon, infrastructure, cabling, connector, and test equipment vendors. Data presented at the CFI indicate a substantial market potential, e.g., the prediction for 2025 is >100 million total ports/year. Version 2.5 Page 4 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD
Compatibility Each proposed IEEE 802 LMSC standard should be in conformance with IEEE Std 802, IEEE 802.1AC, and IEEE 802.1Q. If any variances in conformance emerge, they shall be thoroughly disclosed and reviewed with IEEE 802.1 WG prior to submitting a PAR to the Sponsor. a) Will the proposed standard comply with IEEE Std 802, IEEE Std 802.1AC and IEEE Std 802.1Q? b) If the answer to a) is no , supply the response from the IEEE 802.1 WG. c) Compatibility with IEEE Std 802.3 d) Conformance with the IEEE Std 802.3 MAC As a PHY amendment to IEEE Std 802.3, the proposed project will remain in conformance with IEEE Std 802, IEEE Std 802.1AC, and IEEE Std 802.1Q. The proposed amendment will conform to the IEEE 802.3 MAC. As with other IEEE 802.3 projects, a number of new PHY types will be defined. Version 2.5 Page 5 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD
Distinct Identity Each proposed IEEE 802 LMSC standard shall provide evidence of a distinct identity. Identify standards and standards projects with similar scopes and for each one describe why the proposed project is substantially different. Substantially different from other IEEE 802.3 specifications / solutions. There is no IEEE 802.3 standard that supports electrical Ethernet at rates greater than 10 Gb/s for the requirements of automotive applications. The project may define multiple PHYs, but will define only a single PHY for each rate, media, and link reach combination. Version 2.5 Page 6 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD
Technical Feasibility Each proposed IEEE 802 LMSC standard shall provide evidence that the project is technically feasible within the time frame of the project. At a minimum, address the following items to demonstrate technical feasibility: a) Demonstrated system feasibility. b) Proven similar technology via testing, modeling, simulation, etc. c) Confidence in reliability. The proposed project will build on the array of Ethernet component and system design experience, and the broad knowledge base of Ethernet network operation. Full-duplex operation over a balanced twisted pair and other media has been proven both technically and operationally in deployments at rates from 2 Mb/s and higher. Component vendors, including PHY vendors, cabling vendors and systems vendors have presented data on the feasibility of the necessary components for this project. Proposals which leverage existing technologies have been provided. The reliability of Ethernet components and systems can be projected in the target environments with a high degree of confidence. Version 2.5 Page 7 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD
Economic Feasibility Each proposed IEEE 802 LMSC standard shall provide evidence of economic feasibility. Demonstrate, as far as can reasonably be estimated, the economic feasibility of the proposed project for its intended applications. Among the areas that may be addressed in the cost for performance analysis are the following: a) Balanced costs (infrastructure versus attached stations). b) Known cost factors. c) Consideration of installation costs. d) Consideration of operational costs (e.g., energy consumption). e) Other areas, as appropriate. Ethernet interfaces in the target data rate range defined by this project will maintain a favorable cost-performance balance. The balance of costs between infrastructure and attached stations is not applicable to the automotive environment. The cost factors for Ethernet components and systems are well known. The proposed project may introduce new cost factors which can be quantified. Prior experience in the development of other physical layer specifications for Ethernet indicates that the specifications developed by this project will entail a reasonable cost for the resulting performance. The reduction in the number of legacy networks requiring specialized components, expertise, and gateways in the targeted markets will result in a significant drop in both installation and operational costs. Overall costs are minimized by introducing Ethernet network architecture, management, and software into the automotive environment. Migrating automotive networking to Ethernet results in a significant improvement in system price/performance. Version 2.5 Page 8 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group - CSD