Introduction to Aldehydes and Ketones Nomenclature
Explore the naming conventions for aldehydes and ketones derived from carboxylic acids, along with examples and common names. Understand the nomenclature of organic compounds and aromatic compounds, including benzaldehyde, formic acid, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Aldehydes and Ketones Prepared by Dr.S.Ignatius Arockiam Dept of chemistry
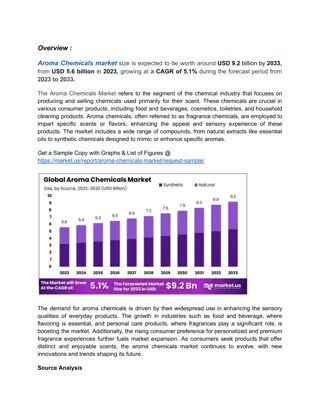
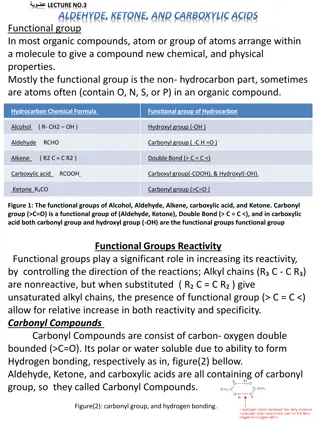
INTRODUCTION Many of the names of aldehydes and ketones are derived from the names of the corresponding carboxylic acids. The information about the nomenclature of carboxylic acids is very useful to give the nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones
Naming of Carboxylic acids O R-COOH, R-CO2H, Common names R COH HCO2H CH3CO2H CH3CH2CO2H CH3CH2CH2CO2H CH3CH2CH2CH2CO2H - - Formic acid - Acetic acid - Propionic acid - Butyric acid Valeric acid
5 4 3 2 1 C C C C C=O used in common names CH3 Br CH3CHCH2COOH CH3CH2CH2CHCOOH bromovaleric acid -methylbutyric acid isovaleric acid
NAMING OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS COOH benzoic acid COOH COOH COOH CH3 CH3 CH3 p-toluic acid m-toluic acid o-toluic acid
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES O carbonyl functional group: C Aldehydes Ketones O O O RCR' HCH RCH R can be Ar
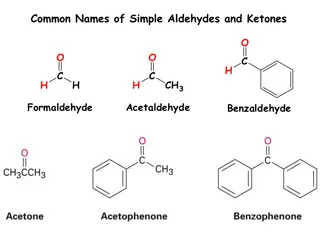
NAMING OF ALDEHYDES FROM THEIR COMMON NAMES (i) To name the aldehydes remove ic acid from the carboxylic acid (ii) add the suffix aldehyde in the end of the compound. CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH=O CH3CHCH=O butyraldehyde ( -methylpropionaldehyde) isobutyraldehyde
CHO CHO CH3 o-tolualdehyde benzaldehyde O CH2CH=O HCH phenylacetaldehyde formaldehyde
NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Select the longest one from the parent chain containing the carbonyl group. Remove the last letter e and then add al in the name of the aldehyde. HCHO - Methanal CH3CHO - Ethanal CH3CH2CH2CHO - butanal CH3CH(CH3)CHO - 2-methylpropanal
COMMON NAMES FOR KETONES O - Dimethyl ketone H3CCCH3 O O O CH3CCH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CCH3 CH3CH2CCH2CH3 methyl n-propyl ketone ethyl methyl ketone diethyl ketone
O Ortho phenones: R C Derived from common name of carboxylic acid, drop ic acid, add (o)phenone. O O H3CC C acetophenone benzophenone
Ketones: IUPAC nomenclature (i) Parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carbonyl group. (ii) drop e, add one. Prefix a locant for the position of the carbonyl using the principle of lower number. O O O CH3CCH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CCH3 CH3CH2CCH2CH3 2-butanone 2-pentanone 3-pentanone
Physical properties: sp2 120o C O C O C O (i)Carbonyl compounds are polar in nature and there is no hydrogen bonding between the atoms (ii)Melting and boiling points are relatively moderate for covalent substances (iii) Compounds are water insoluble . Except the compounds having four carbons or less)
Spectroscopic analysis: IR gives the spectroscopy gives the following strectching frequencies Compound Strectching frequency (cm-1) RCHO 1725 ArCHO 1700 R2CO 1710
Oxidation/Reduction: oxidation numbers increases from alkane to carboxylic acid. oxidation number of the compounds oxidation -4 CH4 CH3OH H2C=O HCO2H alkane alcohol aldehyde carboxylic acid -2 0 +2 reduction