Leukopenia: Causes and Implications
Leukopenia refers to a decrease in white blood cells, which can be caused by various factors such as bone marrow issues, autoimmune disorders, severe infections, and more. This condition can have serious implications on the immune system and overall health.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
LEUKOPENIA BY HUSSEIN ALI NAJI
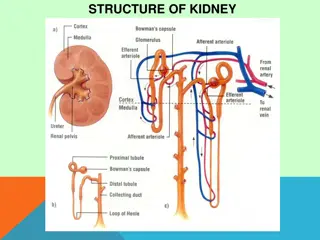
Leukopenia Leukopenia refers to the decrease in the number of white blood cells (WBC) in blood. Causes of Leukopenia Leukopenia may be caused by various diseases and drugs. Some of these are outlined here:- A- Bone marrow damage or suppression This is caused due to exposure to certain chemicals or toxins, cancer chemotherapy, radiation therapy and certain drugs. These agents cause a decrease in production of all the cells of the bone marrow leading to leukopenia, anemia (low number of red blood cell production and platelets).
B- Bone marrow diseases In these conditions the bone marrow does not produce sufficient WBCs or selectively produces excess of one type of WBCs leading to a lack of other types. The causes include myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, myeloproliferative syndrome, myelofibrosis (bone marrow replaced by fibrous tissues), vitamin B12 or folate deficiency etc. C- Cancers that have spread to the bone marrow Cancers when they have spread to the bone marrow may lead to leukopenia. This is seen in lymphomas and other cancers.
D- Autoimmune disorders This occurs when the body fails to recognize its own cells and begins to attack them. In cases of leukopenia the body s WBC s are perceived as foreign and attacked. The condition is called lupus or Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). E- Severe infections Severe infections that deplete the body of WBCs may lead to leukopenia. This is called sepsis.
G- Diseases of the immune system Diseases of the immune system, such as HIV, which destroy T lymphocytes H- Hypersplenism This is caused by enlargement of spleen that destroys the blood cells leading to leukopenia as well as anemia.
Pseudoleukopenia This occurs at the initial phases of the infection. The leukocytes (predominately neutrophils) are responsible for the initial reaction to an infection. After an infection these cells gather around the margins of the blood vessels (marginalized) so that they can scan for the site of infection. Thus there is increased WBC production but it appears low from a blood sample, since the blood sample is of core blood and does not include the WBCs gathered to reach the site of infection.
Neutropenia This term refers to an decreased numbers neutrophiles in blood circulation, under about 4 109 in monogastric animals or about 1 109 in ruminant, this can occur in a numbers way. Viral infection. (e.g., parvovirus in dogs and cats and equine herpesvirus-1 in foals), rickettsial diseases Increasd demand for neutrophils without compensatory inflow from the bone marrow. acute salmonellosis in horses and calves.
neutropenia can occur following the net movement of neutrophils from the CNP to the MNP, as occurs during shock. Hypoplastic conditions associated with neutropenia precursor cells in the marrow include idiosyncratic drug reactions (e.g., phenylbutazone, trimethoprim/sulfadiazine, griseofulvin, cephalosporins, fenbendazole) estrogen toxicity (exogenous or endogenous) in dogs. Increase destruction of neutrophils in circulation. This occur in autoimmune neutropenia. Decreasd bone marrow production.
Eosinopenia This term refers to a decreased numbers eosinopenia in blood circulation, under about 0.1 109 , The absolute eosinophil count may be zero in some normal animals, making eosinopenia of limited significance. Endogenous & exogenous glucocorticoids rapidly induce eosinopenia in animals due to the corticosteroid inhibit mast cells regranulation and so reduced histamine production and prolonged exposure to corticosteroids will reduce bone marrow eosinophil production. Stress including prolonged intensive athletic training, acute stress causes increase catecholamine secretion and chronic stress causes increased corticosteroid secretion.
Lymphopenia This term refers to an decrease numbers of circulating of lymphocyte, below about 1 109 in monogastric animals or about 3 109 in ruminant, this can occur in a numbers way. Steroid effects. Any of reasons for increased circulating corticosteroid ( stress, steroid therapy) Infection. Lymphopenia often accompanies the neutropenia seen in acute viral infections. Neoplasia.