MESA Early Heart Failure Study
Heart failure, a complex spectrum of clinical presentations, is being studied in the MESA Early Heart Failure Study 2020 Update by Sanjiv Shah and Alain Bertoni. The study aims to explore the prevalence, pathogenesis, and phenomics of early heart failure using various assessments and technologies. Understanding early heart failure is crucial for improving patient outcomes and developing effective treatments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MESA Early Heart Failure Study 2020 Update Sanjiv Shah / Alain Bertoni Northwestern/ Wake Forest
HFpEF vs. HFrEF HFrEF HFpEF Left Left Well studied Poorly understood Increasing in prevalence No definitive treatments High morbidity/mortality ventricle ventricle Decreasing in prevalence Many proven treatments Decreasing morbidity Decreasing mortality Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Systolic HF Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction Diastolic HF
What is early heart failure? CLINICAL, SYMPTOMATIC HEART FAILURE IS A SPECTRUM Depends on: (1) type of clinical presentation; (2) MD threshold to hospitalize the patient vs. outpatient treatment OUTPATIENT Dyspnea on exertion due to myocardial problem with evidence of cardiac output and/or LV filling pressures at rest or with exertion INPATIENT CHF hospitalization due to overt volume overload and/or low output state CLINICAL SPECTRUM Traditional HF endpoint in epidemiology studies Potentially underdiagnosed early heart failure
What is early heart failure? Definition of early HF: No prior HF hospitalization and Presence of HF symptoms or functional limitation suggestive of HFand NTproBNP or echo evidence of elevated LV filling pressure (at rest or with passive leg raise preload increase maneuver) We anticipate that most cases of early HF in MESA are early HFpEF
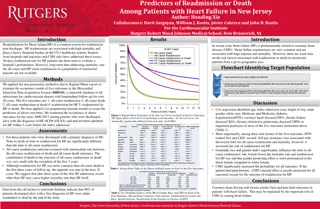
MESA Heart Failure Study (Shah/Bertoni PIs) Specific Aims: Aim 1 (Prevalence): Determine the prevalence of early HF All participants, all 6 sites: Questionnaires: o KCCQ 6MWT Laboratory: NTproBNP, Olink CVD3 proteomics Echocardiography o GE Vivid T8 2D, Doppler, speckle-tracking Resting echo Passive leg raise maneuver Arterial tonometry o Fukuda VaSera Pulse-wave velocity Augmentation index Arterial waveform Substudy: Cardiopulmonary exercise test Aim 2 (Pathogenesis): Examine associations between risk factors, biomarkers, and changes in risk factors with early HF and its pathophysiologic markers: o Cardiac mechanics o Ventricular-arterial coupling o Myocardial pressure-stress relationships Aim 3 (Phenomics): Perform machine learning analyses of previously ascertained MESA quantitative data and relate risk factor phenotypic signatures to pathophysiologic markers and HF subtypes
MESA Exam 6: Final Heart Failure Study Components Arterial Stiffness 309 Physical Activity 361 Site Selected Echo KCCQ-12 6MWT 3: Wake Forest 414 307 361 300 4: Columbia 631 551 549 557 557 458 5: Johns Hopkins 450 419 418 423 423 349 6: Minnesota 568 547 525 555 555 447 7: Northwestern 658 649 634 647 653 509 8: UCLA 573 548 534 554 553 495 3294 100% 3021 92% 2969 90% 3097 94% 3102 94% 2558 78% Total CPET (Wake Forest only): n=135
Diagnosis of HFpEF H2FPEF SCORE We defined AF based on ECG on echo or absence of A waves on mitral inflow (need to update to include all AF) Reddy Y, et al. Circulation 2018
Diagnosis of HFpEF H2FPEF SCORE DERIVATION VALIDATION COMBINED H2FPEF SCORE H2FPEF SCORE H2FPEF SCORE Observed HFpEF prevalence Model-predicted HFpEF probability Reddy Y, et al. Circulation 2018
Distribution of H2FPEF score in MESA H2FPEF Score 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Total N 6 Percent 0.19 13.24 23.77 25.26 18.15 12.65 5.81 0.37 0.22 0.34 Cum. 0.19 13.4 37.2 62.5 80.6 93.3 99.1 99.4 99.7 100 426 765 813 584 407 187 12 7 11 3218 Score Groups 0-4 5 (prob 80%) 6-9 (prob 90%+) Total Freq. 2,594 407 217 3,218 Percent 80.6 12.7 6.7 100 Cum. 80.6 93.3 100
MESA Early Heart Failure Algorithm START NO early HF YES Prior history of HF hospitalization Overt HF NO Symptoms of HF/dyspnea on KCCQ or PROMIS-Dyspnea or 6MWT below age-/gender-cut-offs (limited by dyspnea or fatigue) NO YES History of chronic lung disease or prior abnormal PFTs YES NTproBNP > 250 pg/ml NO YES NO E/e > 15 (septal) or E/e > 10 (lateral) or LA vol. index > 28 ml/m2or LVEF < 40% YES Early HF Possible early HF NO EF < 50% EF > 50% During leg-raise: E/e > 15 (septal) or E/e > 10 (lateral) or LA peak positive strain < 10% increase compared to resting values Early HFrEF Early HFpEF YES NO
Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire Short Version (KCCQ-12) KCCQ: 23-item questionnaire designed to capture HF symptoms and QOL limitations Short version (KCCQ-12; Spertus & Jones 2015) has good psychometric properties Score ranges from 0-100 (0=worst, 100=best) Minimal clinically important difference: 5 points Stable HF Clinic Visit HF N 29 115 115 14 NYHA Class I II III IV N Mean (SD) 86 (15) 73 (19) 50 (21) 29 (29) Mean (SD) 80 (15) 69 (20) 51(22) 28(25) 310 267 80 7
KCCQ-12 summary score results .15 Mean KCCQ-12 score Female 92.1 90.7 87.0 82.4 Age Categories Male 93.6 94.3 90.7 87.2 .1 55-64 65-74 75-84 >=85 Density .05 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 KCCQ-12 SUMMARY SCORE MESA Exam 6 KCCQ-12 summary score: mean 90.4, SD 13.8 KCCQ-12 summary score <80: 15% prevalence KCCQ-12 summary score <85: 20% prevalence
6MWT distance distribution N=2531 .004 .003 Density .002 .001 0 0 200 400 600 800 TOTAL DISTANCE WALKED IN 6 MINUTES (METERS) Mean age 74 years, 53% female, 40% White, 13% Chinese, 25% Black, 22% Hispanic Mean distance: 410 meters (SD 96) 25th percentile: 348 meters Median: 410 meters 75th percentile 476 meters
CHS formula for 6MWD Reference equation for 6MWD from healthy subset of CHS [Enright et al, Chest 2003] For the total distance walked in meters: Women: 493 + (2.2 height [cm]) (0.93 weight [kg]) (5.3 age) Men: same formula except add 17 meters to the calculated value Subtract 100 meters from the calculated value for the lower limit of the normal range
NTproBNP In MESA Exam 6 participants, NTproBNP was assayed using standard ELISA assay (n=1000) and Olink CVD3 proteomic panel (proximity extension assay) (n=3300) and expressed in log2 Normalized Protein eXpression (NPX) units Regression between the two used to estimate NTproBNP level for the entire sample in standard units (pg/ml)
NTproBNP Regression equation: Estimated NTproBNP = e((0.82*Olink NTproBNP) 0.68)
MESA Early Heart Failure Algorithm N=3022 START NO early HF Prior history of HF hospitalization YES N=69 Overt HF NO N=602 with either KCCQ-12 < 80 or 6MWD < CHS lower limit KCCQ12<80: n=442 (15%) Abnormal 6MWD: n=225 (9%) Symptoms of HF/dyspnea on KCCQ or PROMIS-Dyspnea or 6MWT below age-/gender-cut-offs (limited by dyspnea or fatigue) NO YES History of chronic lung disease or prior abnormal PFTs YES 19.5% NTproBNP > 250 pg/ml of entire sample NO YES NO E/e > 15 (septal) or E/e > 10 (lateral) or LA vol. index > 28 ml/m2or LVEF < 40% YES 59% Early HF Possible early HF of entire sample NO EF < 50% EF > 50% During leg-raise: E/e > 15 (septal) or E/e > 10 (lateral) or LA peak positive strain < 10% increase compared to resting values 50% Early HFrEF Early HFpEF of entire sample YES NO
Results From N=3303, excluded: N=69 with previously adjudicated HF N=256 without echocardiogram N=7 without both KCCQ-12 and 6MWT Final sample: N=2956 Algorithm resulted in 602 potential early HF based on KCCQ12 and 6MWD: N=115 did not meet NTproBNP/echo criterion N=489 met criterion for HF Final:N=472 (16%) HFpEF, N=15 (0.5%) HFrEF, N=2469 (83%) no early HF
Results in context Current estimate of HF prevalence in US: N=6.5 million, of which ~50% have HFpEF HFpEF prevalence N=3.25 million 1% of the overall US population 4.7% of US population age > 60 years (68.7M in 2016) H2FPEF score 5 or higher: 12.7% in MESA Est. US prevalence of early HFpEF: n=8.72 million MESA Early HF algorithm: 16% in MESA Est. US prevalence of early HFpEF: 10.9 million There may be up to ~10 million undiagnosed HFpEF patients in the US
Characteristics by HF status Characteristic No HF N=2,469 73.1 51% 41% 14% 24% 21% 63% 22% 32% 5488 62% 4.48 94.8 2137 426 HFrEF N=15 83.5 33% 33% 0% 27% 40% 87% 40% 40% 2273 41% 7.25 62.9 5 292 HFpEF N=472 75.7 64% 33% 13% 29% 25% 80% 33% 42% 3089 63% 5.19 70.5 298 303 P-value Age Female White Chinese Black Hispanic HTN Diabetes Obese (BMI>30) Mod+Vig PA MET-min Ejection Fraction Mean Olink BNP KCCQ12 6MWD, N 6MWD, Meters * * * * * * * * * * * p-value<0.01
Early HF and general health GENERAL HEALTH EXCELLENT % VERY GOOD % GOOD % FAIR % POOR % Total No HF HFrEF HFpEF 331 13.4 967 39.2 858 34.8 295 12.0 17 0.7 2,468 0 0 1 17 3.6 72 15.3 204 43.2 156 33.1 23 4.9 472 6.7 7 46.7 6 40.0 1 6.7 15 Participants classified as early HF less likely to report Excellent or Very Good health
Early HF and lung disease Spirometry normal % obstructive % restrictive % Total Not HF 1,273 62.0 551 26.8 231 11.2 2,055 HFrEF 4 40.0 5 50.0 1 10.0 10 HFpEF 186 49.2 127 33.6 65 17.2 378 Total 1,463 (60%) 683 (30%) 297 (10%) 2,443 Lung disease based on Exam 6 spirometry used FEV1 and FVC to categorize Lung disease and HF overlap is substantial
H2FPEF vs. MESA Early HF algorithm Early HF HFrEF H2FPEF score None HFpEF 0-4 2064 9 333 83.6% 60.0% 70.6% 5 283 2 82 11.5% 13.3% 17.4% 6-9 122 4 57 4.9% 26.7% 12.1% Approximately 2/3rds of sample is low risk/not early HF but otherwise there was not close overlap of 2 schemes
Next steps Examine different cut points for 6MWD and KCCQ12 Add AF information (refine H2FPEF score) Apply the European Society of Cardiology HFA-PEFF diagnostic algorithm (published in 2019) Relies exclusively on echo parameters and NTproBNP levels (with different cut-points for sinus rhythm vs. AF) Once final definition of early HF, utilize CPET data to validate various definitions Investigate association of the usual suspects - race/ethnicity, SES, health habits, obesity, HTN, diabetes, with early HF Examine proteomic differences between no early HF vs. early HFpEF