MOSFET: Types and Operation
Explore the world of MOSFET transistors, including their types like Depletion MOSFET and Enhancement MOSFET. Learn about the operation and differences from JFET, with insights into the depletion mode and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
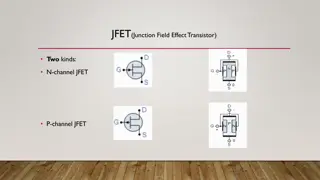
FET MOSFET JFET
MOSFE T
Introduction The MOSFET (metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor) It is another category of field effect transistor . the MOSFET differs from the JFET (junction field effect transistor ) In that it has no p-n junction structure instead ,the gate of the MOSFET is insulated from the channel by the silicon dioxide (SIO2) layer
Types of MOSFET The two basics of MOSFETs are 1.Depletion MOSFET (D-MOSFET) 2.Enhancment MOSFET (E-MOSFET)
Because of insulated gate ,these devices are sometime called as IGFETs
Depletion mosfet One type of MOSFET is the deplition MOSFET The drain and source are diffused into the substrate material then connected by a narrow channel adjcent to the insulated Gate
Both n-channel and p-channel devices are shown in the figure . we will use the n-channel devices to describe the basics operation . The p-channel operation is the same,except the voltage polarities are opposite to those of the n-channel
D-MOSFET types The D-MOSFET can be operated in either of two modes- 1. The depletion mode or 2. The enhancment mode and it sometimes called as depletion /enhancment MOSFET
DEPLITION MODE Deplition mode visualize the gate as one plate of a parallel plate capictor and the channel as the other plate. the silicon dioxide insulating layer is the dieletric with a negative charges on the gate repel conduction electrons from the channel leaving positive ions in their places .there by, n-channel is depleted of some of its electrons , thus decreasing the channel conductivity the greater the negative voltage on the gate the greater deplition of n-channel electrons .
ENHANCMENT MODE With a positive gate voltage ,more conduction electron are attracted into the channel ,thus increasing the channel conductivity
ENHANCMENT MOSFET The E-MOSFET operates only in the enhancment mode and has no deplition mode. It refers construction from the D-MOSFET in that it has no structural channel that substrate extends completely to the SIO2 layer . For an n-channel by creating a thin layer of negative charge in the substrate region adjacent to the SiO2 layer the conductivity of a channel in enhanced by increasing the gate-to- source voltage and thus pulling more electrons into the channel area. For any gate voltage and thus pulling more electrons into the channel area .for any gate voltage below the threshold value ,there is no channel
The voltage at which the surface inversion layer just forms plays an extermely important role in FET and is also called as threshold voltage Vtn. The region of output characteristics where VGStn and no current is called cutt-off region. When the channel forms in Nmos (pMOS) transistor ,a positive(negative) drain voltage with respect to source creates a horizontly electricfeild moving the electrons (holes). and drain current coming to transistor. This continous carrier profile from drain to source are effectively short- circuited.