Definition of WUR Signal Bandwidth
This document discusses the importance of defining the signal bandwidth for Wake-Up Radio (WUR) signals in IEEE 802.11 standards to ensure interoperability and network performance. It covers justifications, methods, and examples related to defining WUR signal bandwidth, emphasizing the need for explicit definitions in the standard draft.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
March 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 Definition of WUR Signal Bandwidth Date: 2019-03-11 Authors: Name Rui Yang Affiliations Address Phone email Rui.yang@interdigital.com 2 Huntington Quad; 4th Floor, South Wing; Melville, NY, 11747 USA Alphan Sahin +1-6316224141 InterDigital, Inc. Submission Slide 1 Rui Yang (InterDigital)
March 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 Abstract This contribution provides justification of why the WUR signal bandwidth needs to be defined and how to do so. Submission Slide 2 Rui Yang (InterDigital)
March 2019 Justification to Define the WUR Signal Bandwidth There are different ways to generate WUR OOK waveform Using .11n/ac OFDM numerology is one of the options To implement a typical WUR receiver (consume < 1mW), e.g., envelope detector, the signal bandwidth needs to be known for designing the radio front-end (e.g., the BPF) of the receiver Specifying the WUR signal bandwidth is important to ensure the interoperability between devices from different vendors and the performance of the network with WUR However, in 11ba D2.0, the WUR signal bandwidth is not explicitly defined doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 Submission Slide 3 Rui Yang (InterDigital)
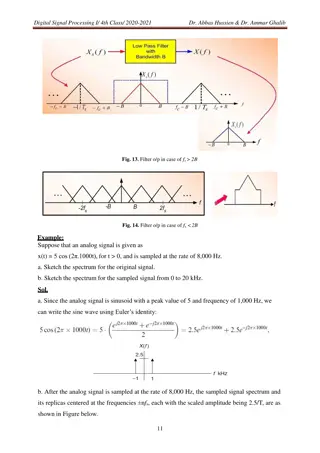
March 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 Method to Define the WUR Signal Bandwidth The bandwidth of a signal can typically defined based on 3-dB (or ?-dB) principle The signal bandwidth in Hertz refers to the frequency range in which the signal s power spectral density is above 3 dB threshold relative to the max within the frequency range Figure copied from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bandwidth_(signal_processing) Submission Slide 4 Rui Yang (InterDigital)
March 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 Examples from Annex AB of D2.0 for LDR B = ~4 MHz Submission Slide 5 Rui Yang (InterDigital)
March 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 Examples from Annex AB of D2.0 for HDR B = ~4.3 MHz Submission Slide 6 Rui Yang (InterDigital)
March 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 Suggestion to the spec draft Add the following text in 31.2.12 (WUR transmit specification) in a new subclause: The 3dB-bandwidth of baseband signals in WUR-Sync, WUR-Data and WUR Padding fields shown in Figure 31- 1(WUR PPDU format), Figure 31-2(WUR FDMA PPDU for 40 MHz channel widths) and Figure 31-3(WUR FDMA PPDU for 80 MHz channel widths) shall not exceed 4.4 MHz. Submission Slide 7 Rui Yang (InterDigital)
March 2019 doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/0381r0 SP Do you agree to the CR for CID 2062 included in IEEE802.11- 19/0382r0? Y/N/A: Submission Slide 8 Rui Yang (InterDigital)