Frequency Division Multiplexing Fundamentals
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) allows multiple signals to be carried simultaneously by modulating them to different carrier frequencies. Channels, subcarriers, and bandwidth allocation are key concepts in FDM systems. Explore the principles and applications of FDM along with other multiplexing techniques such as Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM). Gain insights into how data link capacities are shared efficiently using FDM and related technologies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
FDM,WDM and TDM unit-4 Frequency division multiplexing can be used with analog signals. Synchronous time division multiplexing can be used with both digital signals and analog signals. Statistical time division multiplexing can be used with both digital signals and analog signals. Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 1
Multiplexing How to share the capacity of a data link? FDM: Frequency Division Multiplexing TDM: Time Division Multiplexing Synchronous TDM Statistical TDM Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 2
Frequency Division Multiplexing FDM: A number of signals can be carried simultaneously. Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency Carrier frequencies are sufficiently separated so signals do not overlap (guard bands) Available bandwidth of medium exceeds the sum of all channels Examples: broadcast radio, cable TV Channel allocated even if no data Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 3
Terminologies Channel (FDM): each modulated signal requires a certain bandwidth centered on its carrier frequency, referred to as a channel. Subcarrier: each of the multiple carriers is referred to as a subcarrier. Its frequency is denoted by fi . fi must be chosen so that the bandwidths of various signals do not significantly overlap. Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 4
Frequency Division Multiplexing Diagram Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 5
FDM System n = i B iB 1 Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 6
Wavelength Division Multiplexing Multiple beams of light at different frequency Carried by optical fiber A form of FDM Each color of light (wavelength) carries separate data channel 1997 Bell Labs 100 beams Each at 10 Gbps Giving 1 terabit per second (Tbps) Commercial systems of 160 channels of 10 Gbps now available Lab systems (Alcatel) 256 channels at 39.8 Gbps each, a total of 10.1 Tbps. Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 7
WDM Operation Same general architecture as other FDM Number of sources generating laser beams at different frequencies Multiplexer consolidates sources for transmission over single fiber Optical amplifiers amplify all wavelengths Typically tens of km apart Demux separates channels at the destination Mostly 1550nm wavelength range 50GHz per channel Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 8
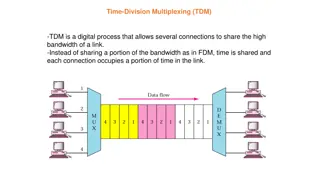
Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing Data rate of medium exceeds data rate of digital signal to be transmitted Multiple digital signals interleaved in time Can be at the bit level or in blocks Time slots pre-assigned to sources and fixed Time slots allocated even if no data Time slots do not have to be evenly distributed amongst sources Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 9
Time Division Multiplexing Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 10
FDM vs TDM Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 11
Terminologies Frames: a cycle of time slots, each of which is dedicated to a data source. Channel (TDM): the sequence of slots dedicated to one source, from frame to frame, is called a channel. Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 12
TDM System N Channels: Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 13
Statistical TDM In Synchronous TDM many slots are wasted Statistical TDM allocates time slots dynamically based on demand Multiplexer scans input lines and collects data until frame full Data rate on line lower than aggregate rates of input lines Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 14
Synchronous TDM vs. Statistical TDM Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 15
Thanks: Prepared by: Neelam Rani, Lect. in Computer Engg.., GPBhiwani 3/18/2025 16