Tissue Sodium and Inflammation Study
Explore the relationship between tissue sodium, inflammation, and blood pressure in the MESA study conducted by Vanderbilt University. The research aims to define tissue sodium distribution, investigate its association with blood pressure, and examine its correlation with Th17 inflammation markers. Utilizing 23Na-MRI technology, the study involves measuring skin and muscle sodium concentrations, assessing blood pressure levels, and analyzing cellular markers of inflammation. Gain insights into the impacts of tissue sodium on health outcomes in middle-aged to elderly individuals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
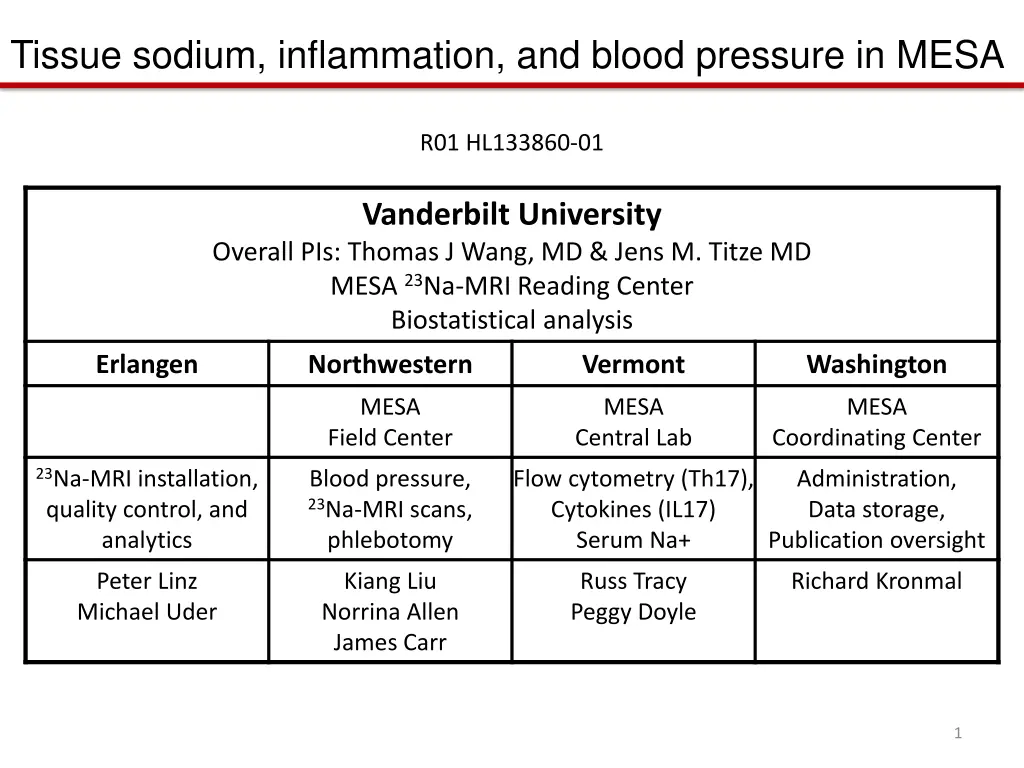
Tissue sodium, inflammation, and blood pressure in MESA R01 HL133860-01 Vanderbilt University Overall PIs: Thomas J Wang, MD & Jens M. Titze MD MESA 23Na-MRI Reading Center Biostatistical analysis Erlangen Northwestern Vermont Washington MESA Field Center MESA Central Lab MESA Coordinating Center 23Na-MRI installation, quality control, and analytics Blood pressure, 23Na-MRI scans, phlebotomy Flow cytometry (Th17), Cytokines (IL17) Serum Na+ Administration, Data storage, Publication oversight Peter Linz Michael Uder Kiang Liu Norrina Allen James Carr Russ Tracy Peggy Doyle Richard Kronmal 1
Specific Aims Aim 1. Todefine the distribution of tissue Na+ content in middle-aged to elderly individuals in thecommunity. We will non-invasively quantify skin and muscle Na+ concentration using 23Na-MRI in MESA participants at the Chicago, IL field center during exam 6 (2016-2018). Aim 2. To investigate the association of tissue Na+ levels with blood pressure. Blood pressure will be measured in MESA participants and the association between skin Na+ concentration and systolic blood pressure will be examined in multivariable-adjusted linear regression analyses. Aim 3. To examine the association of tissue Na+ with Th17 and other cellular markers of inflammation. Circulating immune cells, including Th17 cells, will be quantified via flow cytometry among MESA participants who undergo 23Na-MRI. The association between skin Na+ concentration and Th17 cells will be examined in multivariable-adjusted linear regression analyses. 3
Distribution & correlates of skin sodium 28 15 26 Skin Na (mmol/L) 10 24 Percent 22 5 20 18 0 60 70 80 90 10 20 30 40 50 Age (years) Skin Na (mmol/L) 50 40 40 Skin Na (mmol/L) Skin Na (mmol/L) 30 30 20 20 10 10 0 0 Male Female White Black
Pulse pressure & skin sodium 30 Skin Na (mmol/L) 25 20 15 20 40 60 80 100 Pulse pressure (mm Hg) Adjusted for age, sex, race, HTN med, SBP, BMI, muscle sodium